Primary hyperparathyroidism
Etiology
- Parathyroid gland adenoma (∼ 85%): benign tumor of the parathyroid glands
Clinical features
Symptomatic patients often have clinical features of hypercalcemia
Clinical features
- Nephrolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis (calcium oxalate > calcium phosphate stones)
- Bone pain, arthralgias, myalgias, fractures
- Because most of the calcium is released from bones
- Constipation
- Increase in extracellular Ca2+ → membrane potential outside is more positive → more amount of depolarization is needed to initiate action potential → decreased excitability of muscle and nerve tissue
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Anorexia
- Peptic ulcer disease
- hypercalcemia-induced increase of gastric acid secretion and gastrin levels.
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms such as anxiety, depression, fatigue, and cognitive dysfunction
- Diminished muscle excitability
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- ECG: Shorten QT interval, see ECGs > QT interval
- Muscle weakness, paresis
- Polyuria and dehydration
- Due to acquired renal ADH resistance. Although ADH is being secreted, the kidneys no longer respond to it adequately (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus).
Link to original
Diagnostics
X-ray
- Decreased bone mineral density
- Cortical thinning: especially prominent in the phalanges of the hand; manifests as acroosteolysis (a subperiosteal pattern of bone resorption)
- Unlike the typical osteoporosis of aging, which predominantly affects trabecular bone
- Salt and pepper skull: granular decalcification manifesting as diffusely distributed lytic foci on imaging of the calvarium
- Features of osteitis fibrosa cystica
Complications
Osteitis fibrosa cystica (OFC)
- A rare skeletal disorder seen in advanced hyperparathyroidism characterized by replacement of calcified bone with fibrous tissue
- Most commonly seen in primary hyperparathyroidism but can also occur in secondary hyperparathyroidism
- ↑ PTH → ↑ RANK ligand expression → activation of osteoclasts → bone resorption, cortical bone destruction, and fibrous tissue deposition
- Features include bone pain, subperiosteal thinning, and bone cysts; multiple bone cysts in the skull may result in a salt and pepper skull (pepper pot) appearance on x-ray.
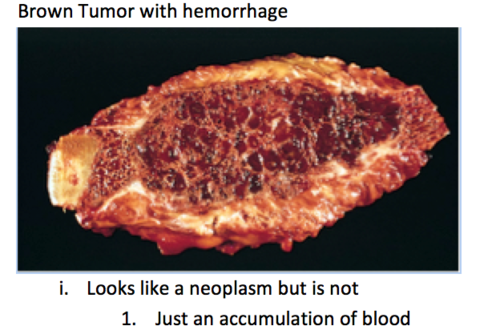
- In advanced OFC, large, cystic, vascular cavities with a tumor-like appearance on x-ray and a brown color due to hemosiderin deposition (brown tumors) can form in long bones.