ACh is the main player.
- Somatic (Motor): ACh (single neuron)
- Parasympathetic: ACh → ACh
- Sympathetic (Standard): ACh → NE
- Sympathetic (Sweat Glands): ACh → ACh
- Sympathetic (Adrenal Medulla): ACh (pre only, no post)→ Epi/NE (blood)
| System | Preganglionic Neuron Neurotransmitter | Postganglionic Neuron Neurotransmitter / Adrenal Medulla Release | Target Organ(s) / Systemic Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor (Somatic) | ACh (Single motor neuron) | N/A (No postganglionic neuron) | Skeletal Muscle |
| Sympathetic | ACh | 1. Typical Targets: NE (α/β adrenergic receptors) 2. Eccrine (Thermo): ACh (M receptors) 3. Apocrine/Stress Eccrine: NE (α1 adrenergic receptors). Also sensitive to circulating Epi/NE. 4. Adrenal Medulla: Hormones (primarily Epi, some NE) into bloodstream | 1. Smooth/Cardiac muscle, Glands; Contraction/Relaxation, ↑HR/Force, Secretion 2. ↑Thermo Sweating 3. ↑Stress Sweating 4. Systemic “Fight/Flight” effects |
| Parasympathetic | ACh | ACh (M receptors). | Smooth/Cardiac muscle (↓HR), Glands (“Rest & Digest” functions) |
Tip
Anticholinergic toxidrome and sympathomimetic toxidrome share most syndromes, except sweat gland.
| Drug Class | Examples | Skin Findings | Bowel Sounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anticholinergic | Diphenhydramine, TCAs, Atropine | Dry | Decreased/Absent |
| Sympathomimetic | Cocaine, Amphetamines, Meth | Sweaty | Increased/Hyperactive |
| Neurotransmitter & Receptor Pair | Functions in the CNS |
|---|---|
| Ionotropic: Ligand-gated ion channels | Transmembrane proteins that allow ions to cross the membrane |
| Glutamate [E] → NMDA receptor: Ca2+ & Na+ influx | Long-term potentiation of learning & memory |
| GABA [I] → GABAA receptor: Cl− & HCO3− influx | Sedation, anxiolytic & anticonvulsive |
| Glycine [I] → Glycine receptor: Cl− influx | Inhibit spinal interneurons (prevents spasticity) |
| Metabotropic: G protein-coupled receptors | Act through second messengers (eg, cAMP, PKA) |
| Dopamine → D1-5 receptors | Modulate attention, movement & reward |
| Serotonin → 5-HT receptors | Modulate mood, nausea & trigeminovascular nociception (migraine) |
| Norepinephrine → α & β adrenoceptors | Promotes vigilance, attention & emotional memory |
| Histamine → H3 receptors | Promotes wakefulness |
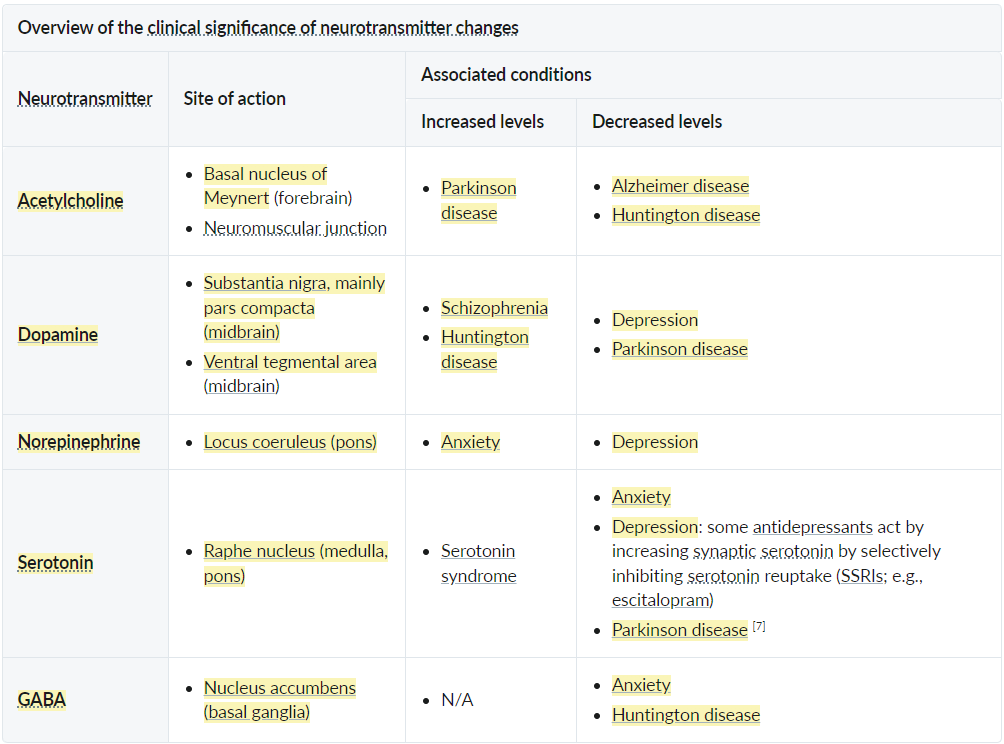
- Acetylcholine
- Usually excitatory
- Increased levels
- Decreased levels
- Alzheimer disease, Acetylcholine and Alzheimer’s both start with A
- Huntington disease
- Dopamine
- Drive to GET a reward. NOT the feeling of reward. Both excitatory and inhibitory
- D1 receptor: Subsequent activation of protein kinase A causes smooth muscle relaxation
- D2 receptor: located mainly in the substantia nigra, striatum, area postrema, and pituitary gland.
- See dopaminergic pathway
- Increased levels
- Decreased levels
- Depression
- Parkinson disease
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (D2 receptor blocked)
- Drive to GET a reward. NOT the feeling of reward. Both excitatory and inhibitory
Functions of dopamine
D rugs psych O sis P rolactin inhibition A ttention M otivation I nvoluntary movements N ausea E nergy
- Norepinephrine
- Alertness
- Increased levels
- Anxiety
- Decreased levels
- Depression
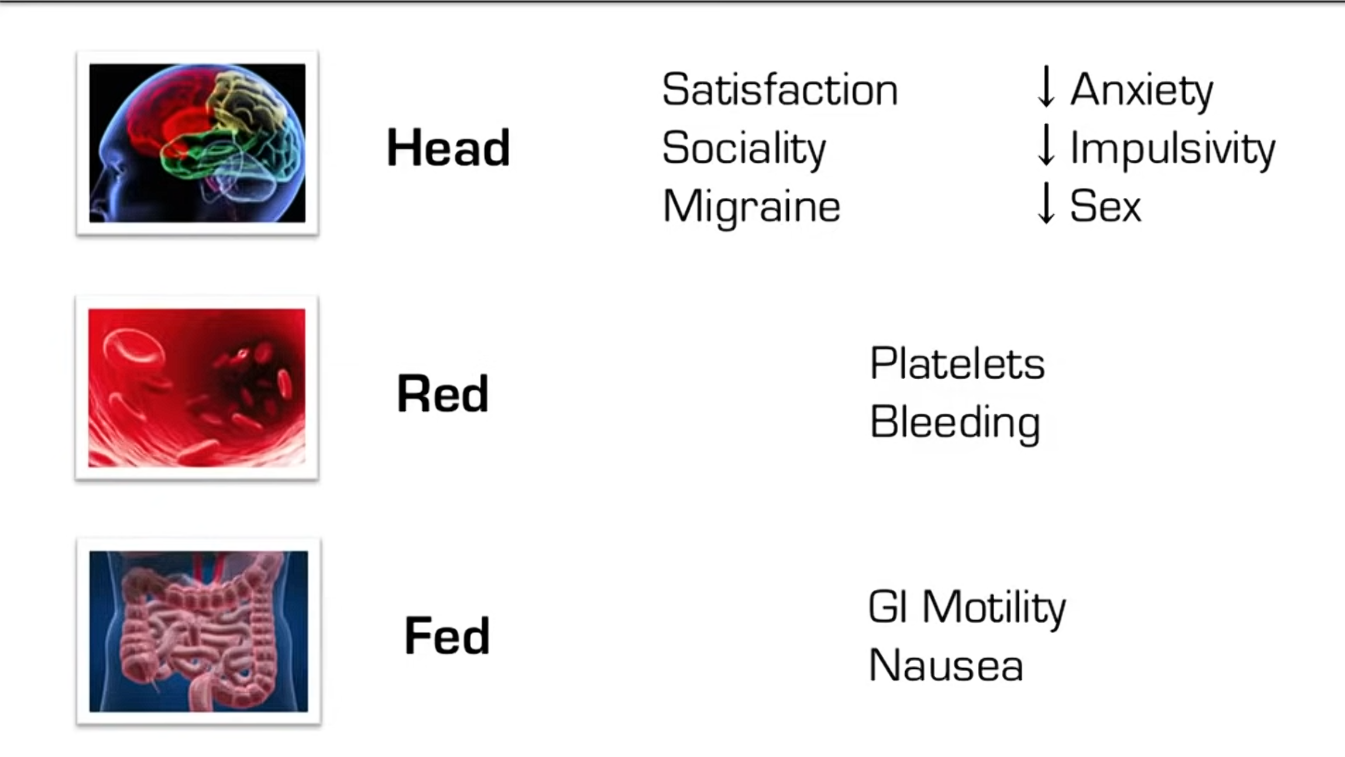
- Serotonin (aka 5-HT)
- Synthesis & Metabolism
- Precursor: Tryptophan
- Locations of Synthesis:
- Primarily in enterochromaffin cells of the GI tract (~90%).
- Also in raphe nuclei of the brainstem. t
- Rate-limiting enzyme: Tryptophan hydroxylase
- Cofactors: Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), O₂, Fe²⁺ t
- Breakdown: By MAO into 5-HIAA (measured in urine for carcinoid syndrome).
- Satiety, Tranquilty, Peace
- Increased levels
- Decreased levels
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Parkinson disease
- Synthesis & Metabolism
- GABA
- GABA A receptor mediates a fast response to GABA because it is an ion-gated chloride channel. Activation of this receptor leads to rapid muscle relaxation and sedation. Its activity is enhanced by benzodiazepines, which can be used to treat spasticity.
- GABA B receptor mediates a slower response to GABA because it is mediated by a G protein–coupled receptor that opens potassium channels. It is agonized by baclofen, which can also be used to treat spasticity.
- Inhibitory in the brain
- Increased levels
- Decreased levels
- Anxiety
- Huntington disease
- Histamine
- Wakefulness. Think about benadryl (antihistamine) makes us drowsy and sleepy)
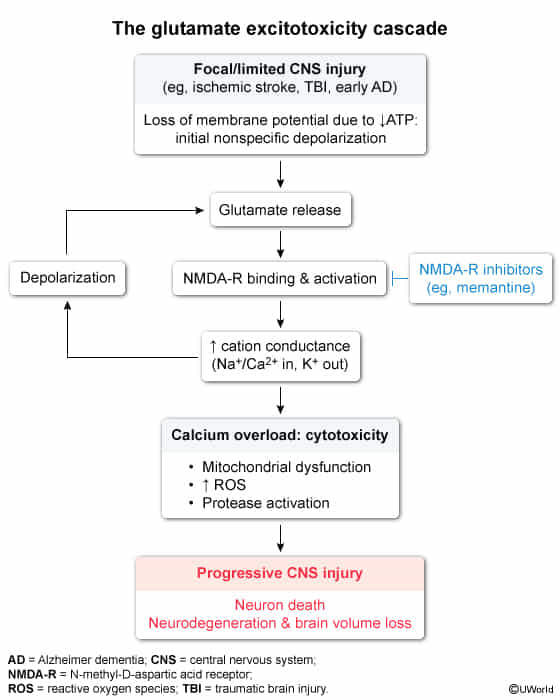
- Glutamate
- The primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS.
- Receptors: NMDA, AMPA, Kainate.
- Clinical Correlation: Excitotoxicity (e.g., in stroke) is mediated by excessive glutamate release, leading to ↑ intracellular Ca2+ and subsequent neuronal death.
- GlutaMATE

- GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)
- The primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS (brain).
- Synthesized from glutamate by glutamate decarboxylase (requires Vitamin B6).
- Receptors:
- GABA-A: Ligand-gated Cl⁻ channel. Target for Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates, and alcohol.
- GABA-B: G-protein coupled receptor.
- Glycine
- The primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cord.
- Receptors: Ligand-gated Cl⁻ channel.
- Clinical Correlation: Strychnine is an antagonist, causing massive tetanic contractions.
| Feature | GABA | Glycine |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Location | Brain | Spinal Cord & Brainstem |
| Precursor | Glutamate | Serine |
| Receptor Blocked by | Bicuculline | Strychnine |
| Dual Role | No (purely inhibitory) | Yes (inhibitory + co-agonist at NMDA receptors) |
| Disease Example | Seizures, Anxiety (low GABA) | Tetanus, Strychnine poisoning (blocked glycine action) |