ToRCHHeS
| Feature | Toxoplasma gondii | Rubella | Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | HIV | HSV-2 | Syphilis | Streptococcus (GBS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Type | Parasite | Virus | Virus (Herpesvirus) | Virus (Retrovirus) | Virus (Herpesvirus) | Bacterium (Treponema pallidum) | Bacterium (Streptococcus agalactiae) |
| Classic Triad/Presentation | Chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications | Cataracts, heart defects, sensorineural hearing loss | No classic triad, but periventricular calcifications, microcephaly, and SNHL are characteristic. | No classic triad; failure to thrive, recurrent infections, and developmental delay are common | No classic triad; skin/mucous membrane lesions, encephalitis, or disseminated infection characterize. | Early: “Snuffles,” rash, bone lesions, lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly; Late: Hutchinson teeth, interstitial keratitis, saddle nose, saber shins | Early-onset: Respiratory distress, sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis (within first week, usually <24 hrs); Late-onset: Bacteremia, meningitis (after first week) |
| Other Key Differentiators | Often asymptomatic at birth, later chorioretinitis. Linked to cat feces/undercooked meat. | ”Blueberry muffin” rash, often mild maternal illness. Preventable by MMR vaccine. | Most common congenital viral infection. Hearing loss can be late-onset. | Opportunistic infections are a hallmark. ART is crucial for prevention. | Vesicular lesions (but not always present). Often acquired during birth. | Multisystem; early/late manifestations differ. Penicillin is treatment. | Leading cause of neonatal sepsis/meningitis. Maternal colonization is key risk factor. Intrapartum antibiotics prevent early-onset disease. |
| Transmission | Transplacental, ingestion | Transplacental, respiratory | Transplacental, body fluids | Transplacental, birth, breastfeeding | Primarily during birth | Transplacental, birth | Vertical transmission during birth (primarily), ascending infection, rarely nosocomial/community-acquired (late-onset) |
Congenital rubella infection
Clinical features
- Intrauterine rubella infection: miscarriage, preterm birth, fetal growth restriction (especially likely if infection occurs during the first trimester)
- Congenital rubella syndrome
- Triad of congenital rubella syndrome
- Cardiac defect: most common defect (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis)
- Cataracts: Other eye manifestations may also occur later in life, including glaucoma and salt and pepper retinopathy (abnormal retinal pigmentation)
- Cochlear defect: bilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- Early features
- Hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice
- Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia
- Petechiae and purpura, i.e., blueberry muffin rash (due to extramedullary hematopoiesis in the skin)
- Late features
- CNS defects: microcephaly, intellectual disability, panencephalitis
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Triad of congenital rubella syndrome
Mnemonic
CCC-Triad of congenital rubella syndrome: Cataracts, Cochlear defects, Cardiac abnormality
- Prevention
- Maternal preconception immunization with live attenuated rubella vaccine
Congenital syphilis
Pathogen
Treponema pallidum
Transmission
- Fetus: transplacental transmission from infected mother
- Neonate: perinatal transmission during birth
Clinical features of congenital syphilis
- Perinatal
- Intrauterine fetal demise
- Prematurity, low birth weight
- Focal necrosis of the umbilical cord
- Mucocutaneous
- Snuffles: copious rhinorrhea, often purulent or serosanguineous
- Desquamating, maculopapular rash involving palms/soles
- Fissures near orifices (eg, anal, oral)
- Jaundice
- Musculoskeletal
- Long bone abnormalities (eg, periosteal thickening, metaphyseal erosion)
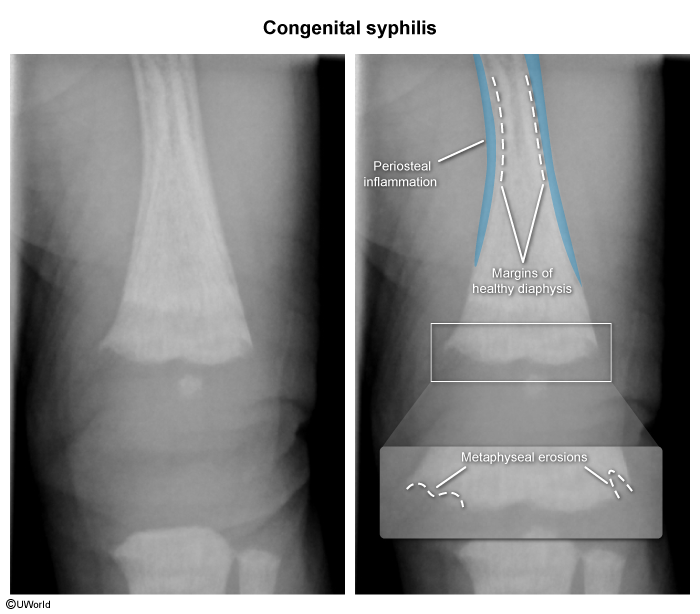
- Bilateral and symmetric metaphyseal erosions and periosteal inflammation of long bones
- Pathologic fractures
- Swelling, pain, and limited movement of affected extremities
- Long bone abnormalities (eg, periosteal thickening, metaphyseal erosion)
- Reticuloendothelial
- Hepatomegaly ± splenomegaly
- Lymphadenopathy
- Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia/leukocytosis