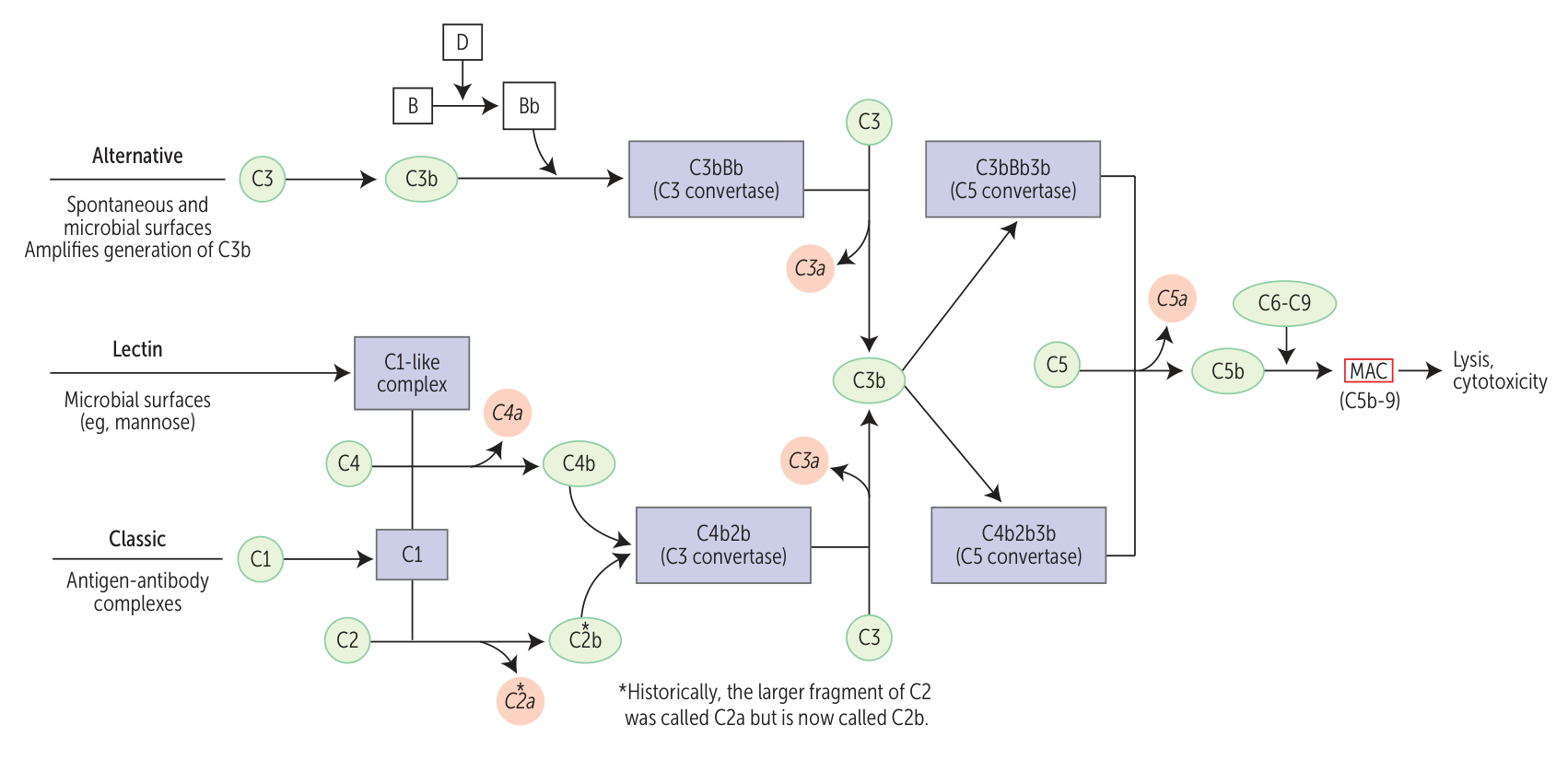
- Activation pathways
- Classical pathway
- Activated by IgM or IgG complexes binding to the pathogen
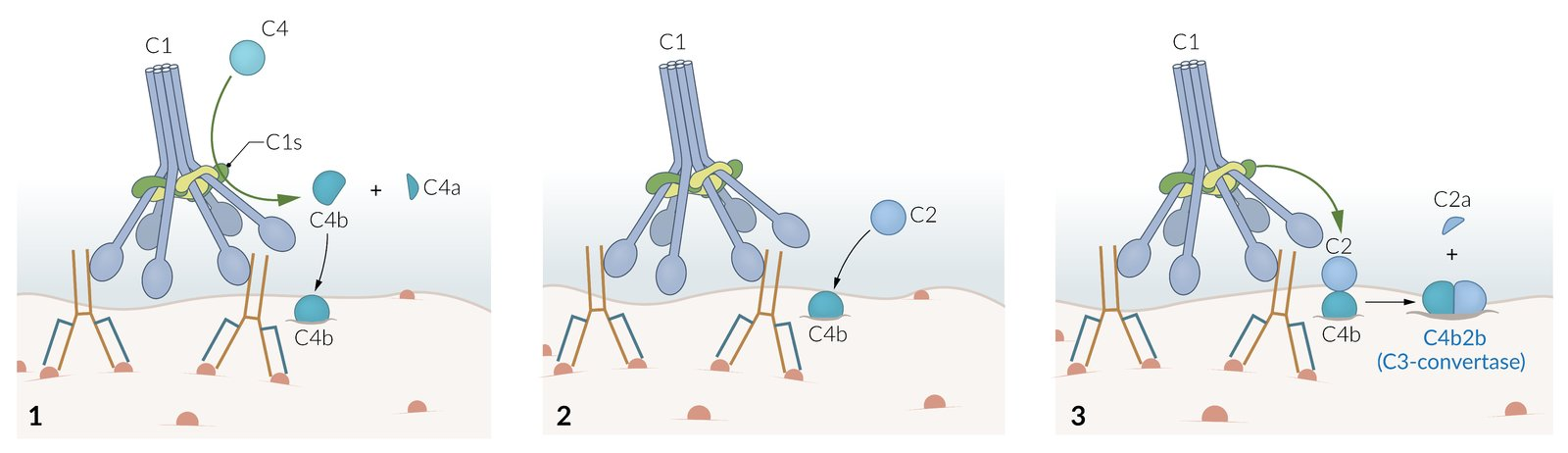
- Activated by IgM or IgG complexes binding to the pathogen
- Classical pathway
- Effect
- Membrane attack complex (MAC)
- Formed by C5b–C9
- Lysis of bacteria (especially gram‑negative bacteria) by perforation of the cell wall
- Opsonization
- Increases the susceptibility of target particles (e.g., bacteria) to phagocytosis
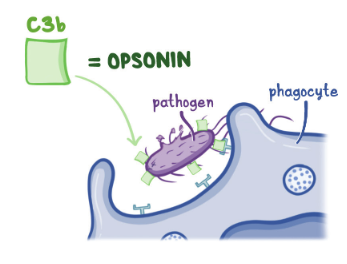
- Attachment of opsonins (e.g., immunoglobulins) causes structural changes that facilitate interaction with immune cells.
- C3b and IgG are the two main opsonins for bacteria
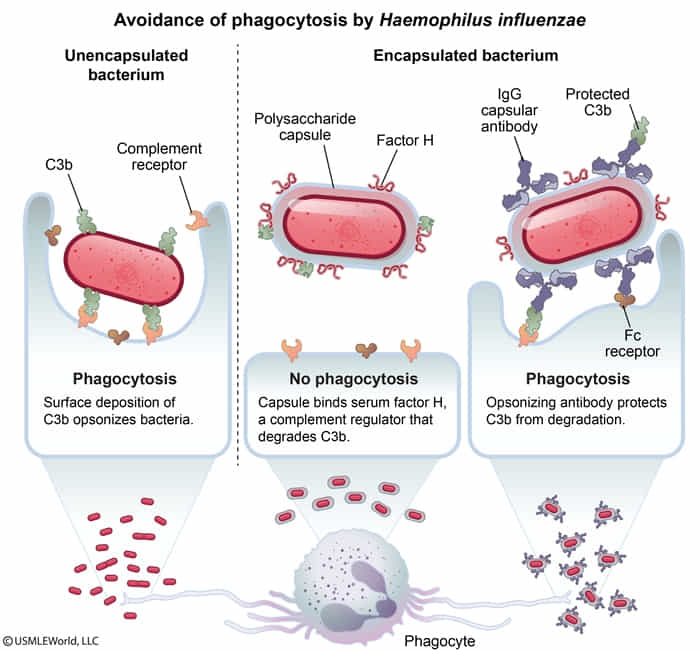
- C3b is also involved in eliminating immune complexes.
- Increases the susceptibility of target particles (e.g., bacteria) to phagocytosis
- Anaphylaxis: activation of mast cells and granulocytes via C3a/C4a/C5a
- Chemotaxis: attraction of neutrophils via C5a
- Membrane attack complex (MAC)
Mnemonic
- C3b binds to bacteria.
- C3a, C4a, C5a lead to mast-cell activation and anaphylaxis.
Complement disorders
C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency
Just think it as C1 inhibitor, as it actually has nothing to do with esterase.
- Etiology
- Autosomal dominant inheritance
- Unregulated activation of kallikrein → ↑ bradykinin → angioedema
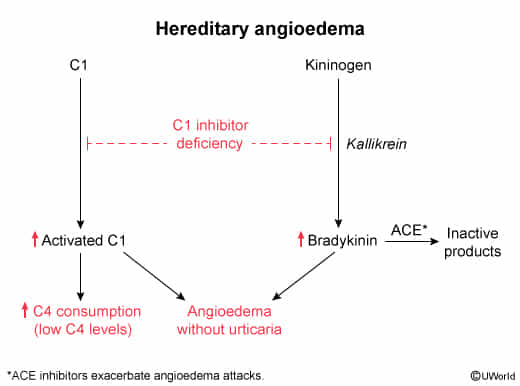
- Clinical features
- Causes hereditary angioedema
- Recurrent angioedemas provoked by triggers (e.g., trauma, surgery, infections, and drugs)
- Not associated with itching or urticaria
- Not involve histamine, which is released in Type I hypersensitivity reaction by mast cells
- Causes hereditary angioedema
- Diagnostic findings
- ↑ Bradykinin levels
- Low C4 levels
- Strong contraindication for ACE inhibitors
Complement deficiencies
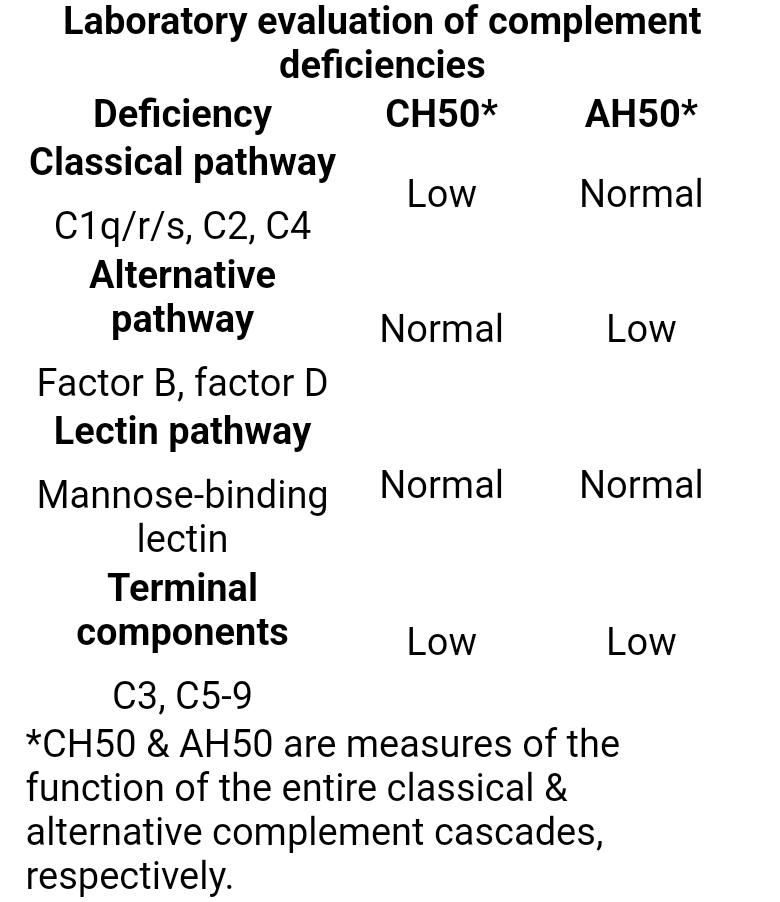
- Recurrent, severe childhood infections (e.g., upper respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, meningitis) with encapsulated bacteria (e.g., N. meningitidis, H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae)