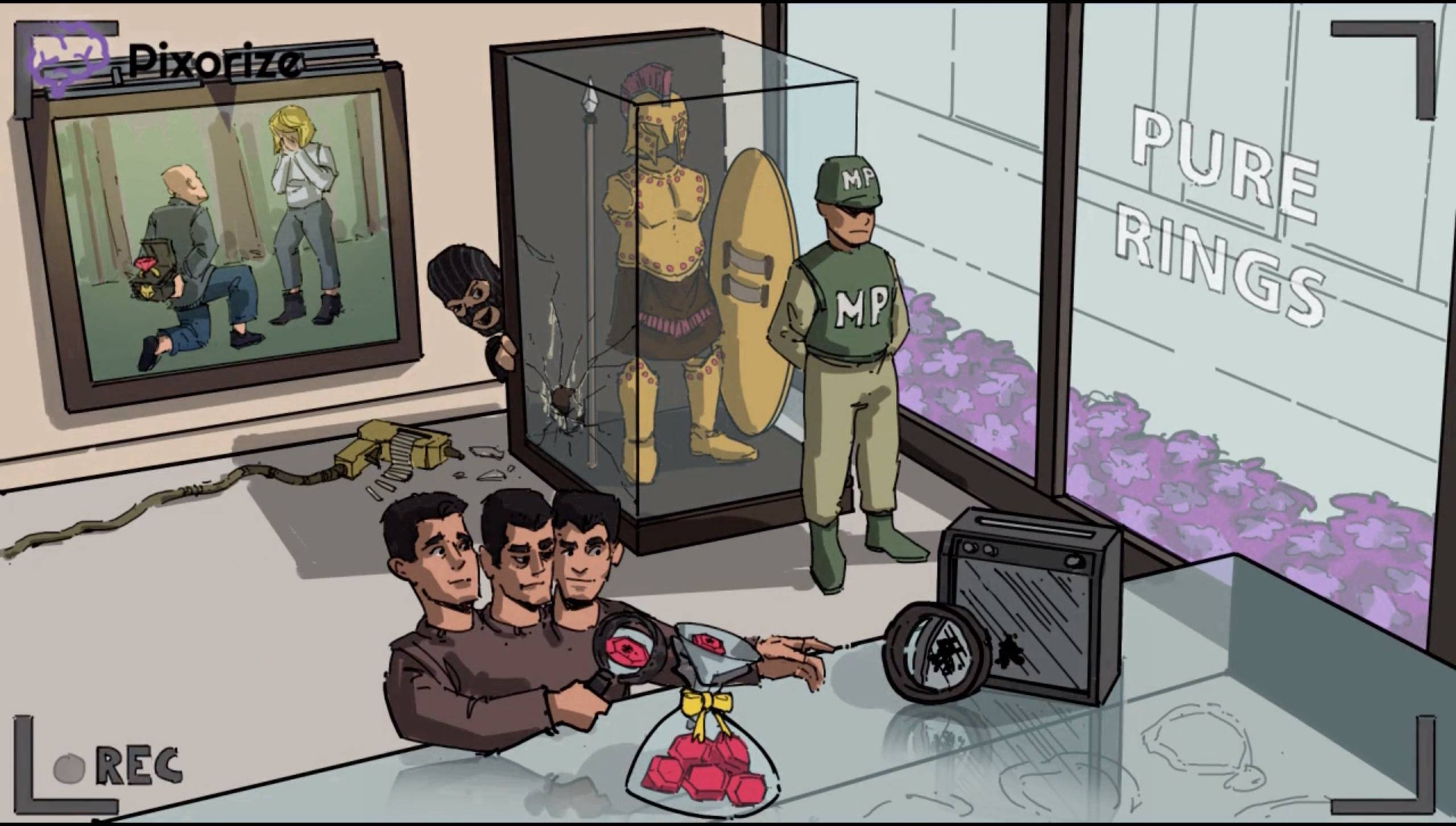
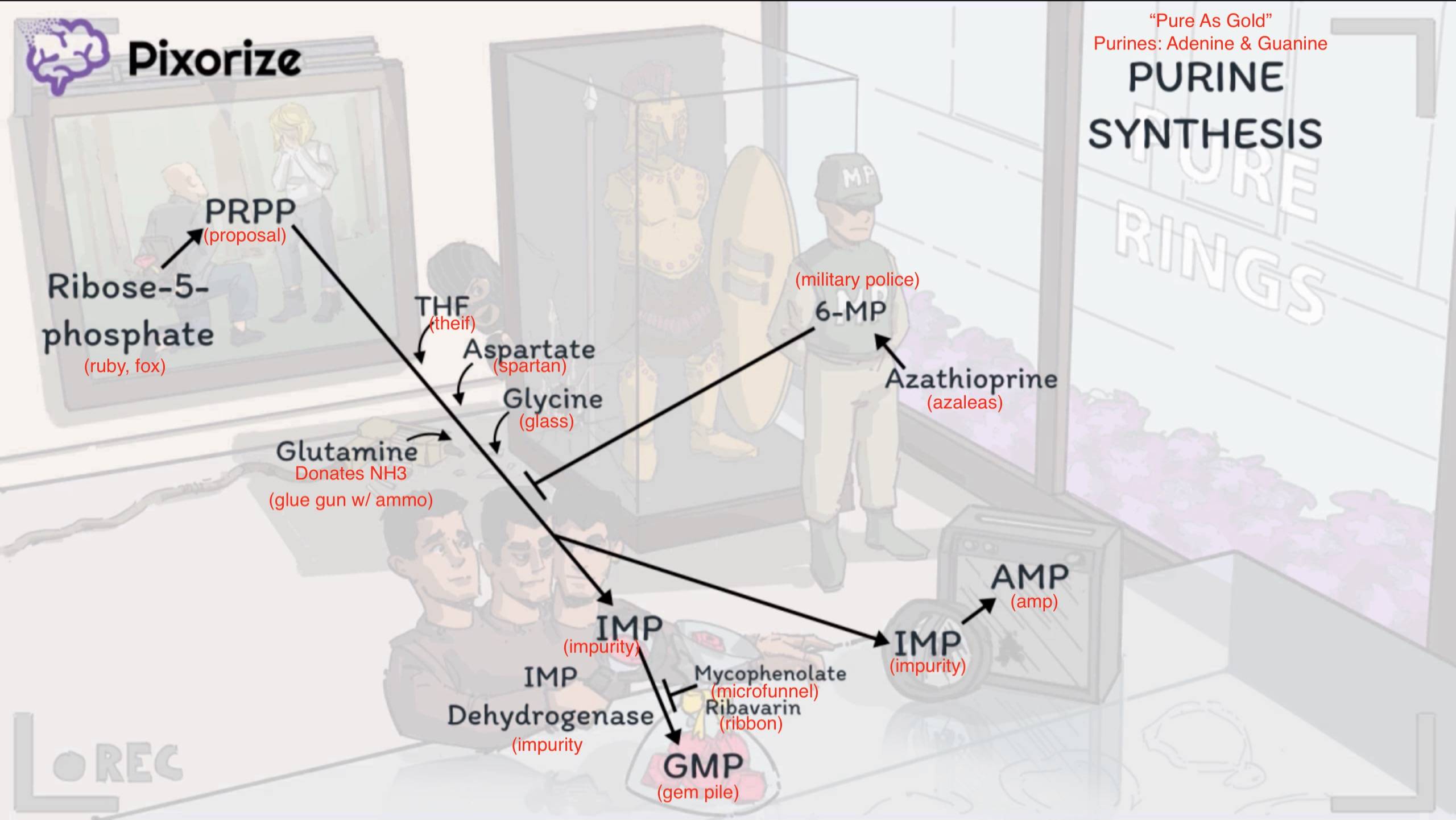
Purine synthesis

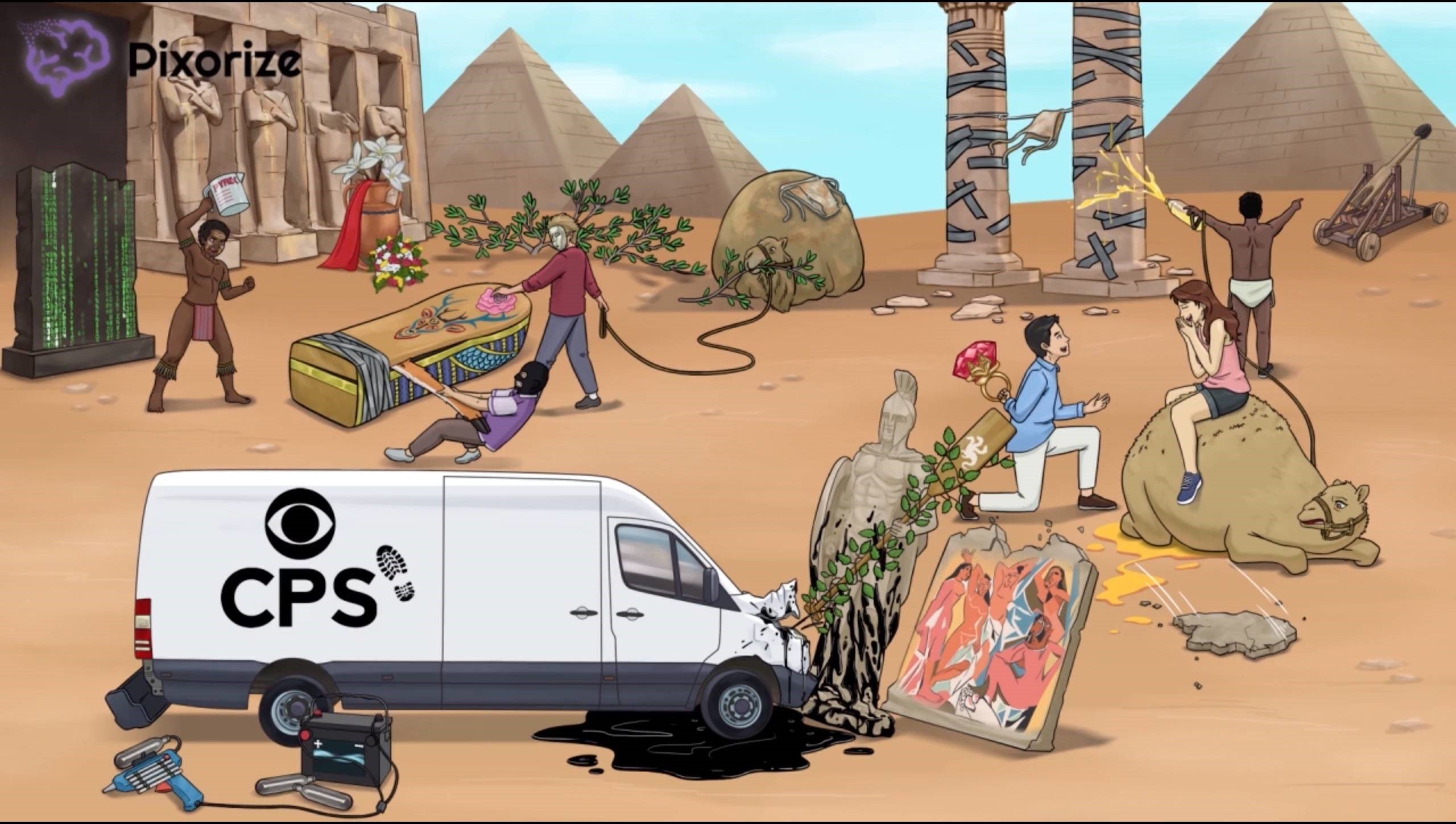
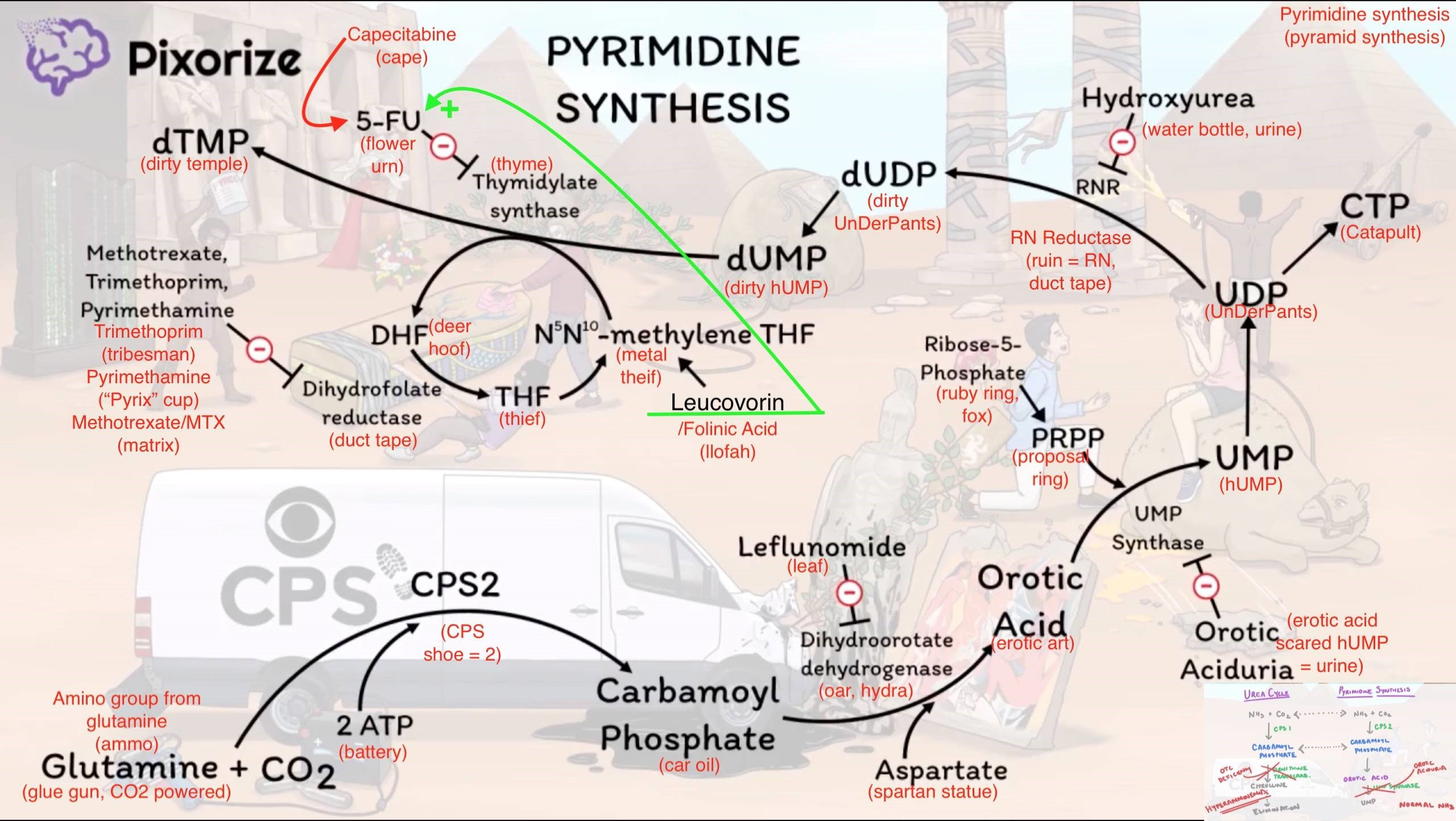
Pyrimidine synthesis

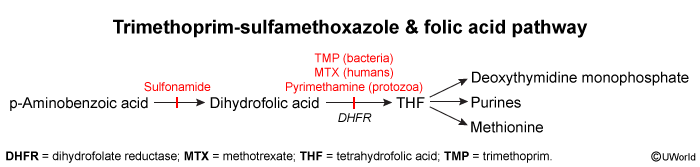
 Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) is a folic acid precursor in prokaryotes. Sulfonamide antibiotics are chemical analogues of PABA that inhibit the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, preventing bacterial conversion of PABA to folic acid. Humans lack the ability to convert PABA to folic acid and require dietary folate.
Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) is a folic acid precursor in prokaryotes. Sulfonamide antibiotics are chemical analogues of PABA that inhibit the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, preventing bacterial conversion of PABA to folic acid. Humans lack the ability to convert PABA to folic acid and require dietary folate.
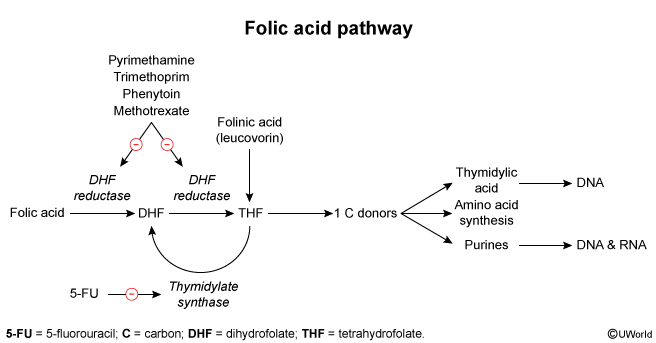
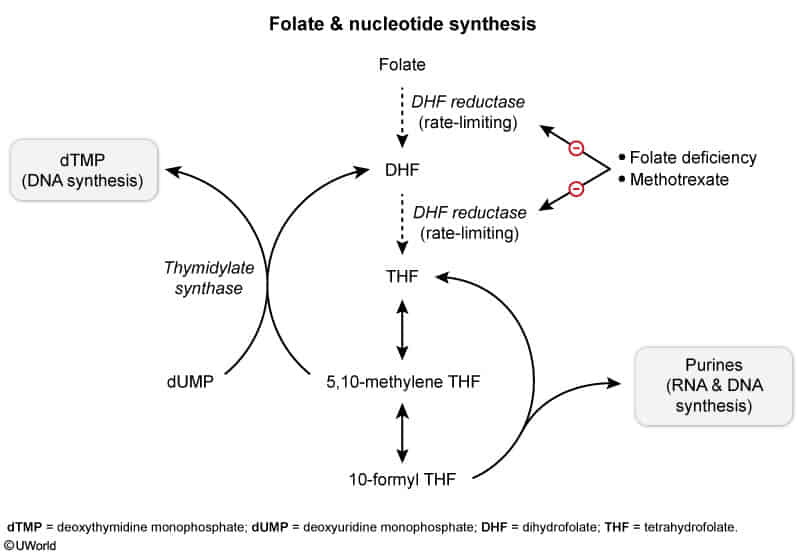 The enzyme thymidylate synthase is responsible for converting deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Although most enzymes involved in one-carbon metabolism maintain folate in its active tetrahydrofolate form, thymidylate synthase is unique in that it oxidizes 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to dihydrofolate. This makes de novo thymidine synthesis particularly susceptible to folate-deficient conditions because tetrahydrofolate must be continuously regenerated by dihydrofolate reductase.
The enzyme thymidylate synthase is responsible for converting deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Although most enzymes involved in one-carbon metabolism maintain folate in its active tetrahydrofolate form, thymidylate synthase is unique in that it oxidizes 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to dihydrofolate. This makes de novo thymidine synthesis particularly susceptible to folate-deficient conditions because tetrahydrofolate must be continuously regenerated by dihydrofolate reductase.