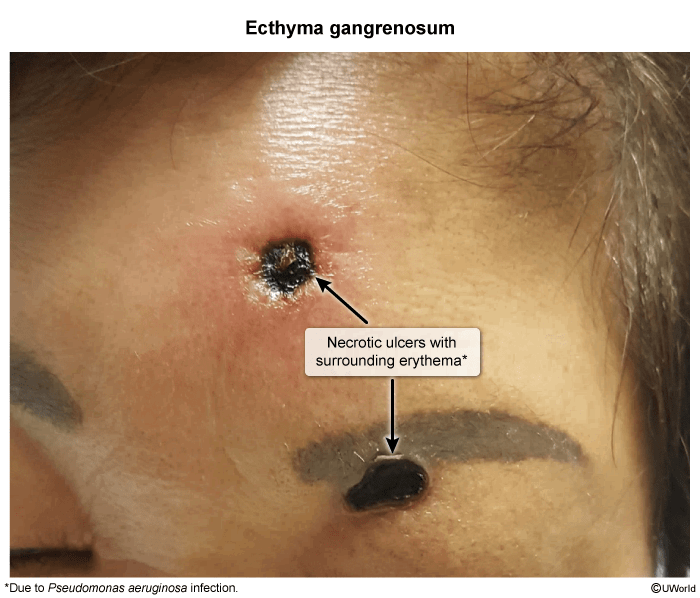
- Definition: an ulcerative lesion extending into the dermis that develops in the setting of bacteremia
- Pathogen: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (not pathognomonic but is the most common causative organism)
- Pathophysiology:
- Classically develops in patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia who are immunocompromised
- Bacteria invade vasculature, causing septic vasculitis and cutaneous necrosis
- Virulence factors destroy tissue:
- Exotoxin A: inhibits elongation factor 2, impairing protein synthesis
- Elastase: degrades elastin in blood vessel walls
- Phospholipase C: breaks down cell membranes
- Clinical features
- Rapid progression (within 12–18 hours) of painless red macules → induration, development of pustules, vesicles, and/or bullae → crusted ulcers