Key Point
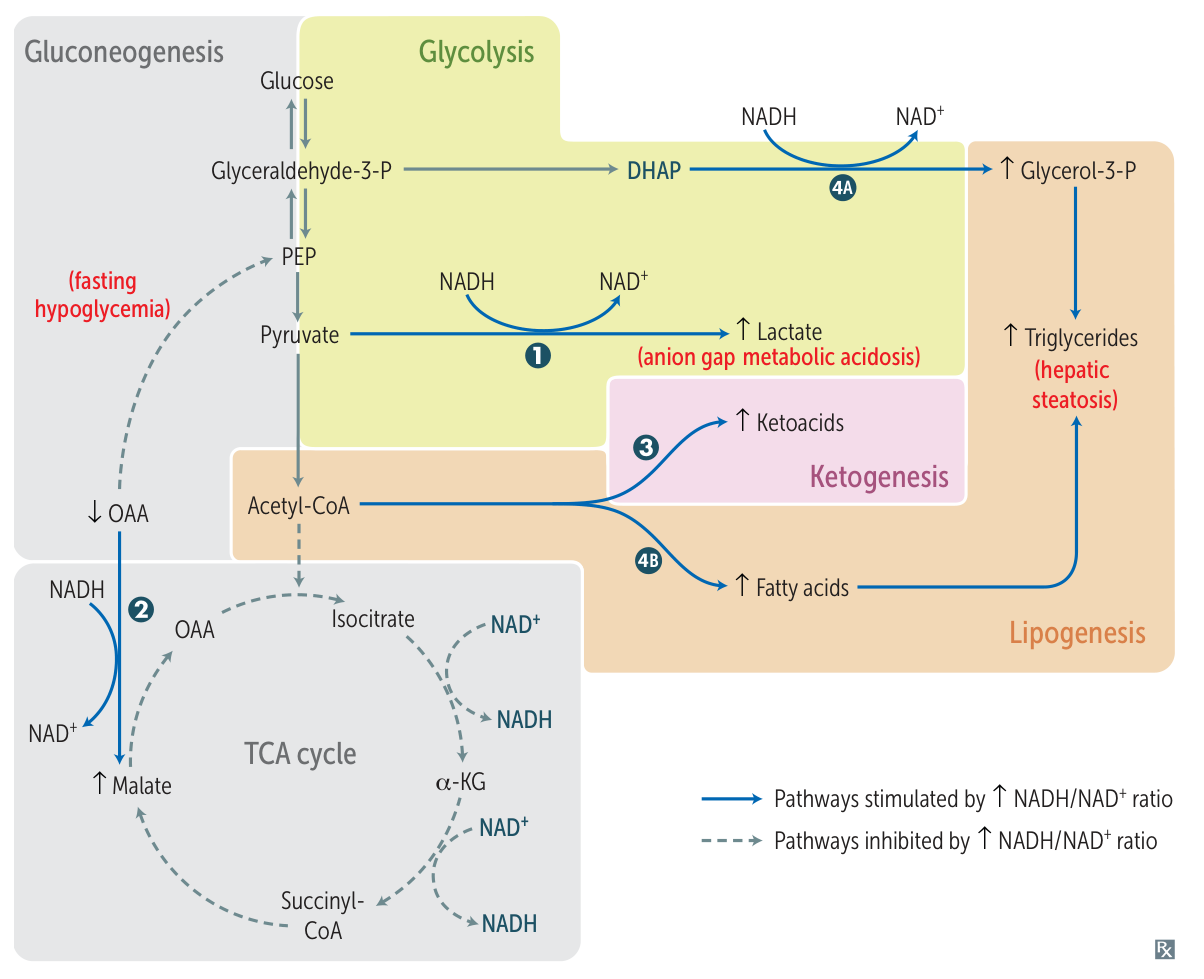
Ethanol metabolism increase NADH/NAD+, which further downregulate gluconeogenesis and TCA cycle, and increase lactate.
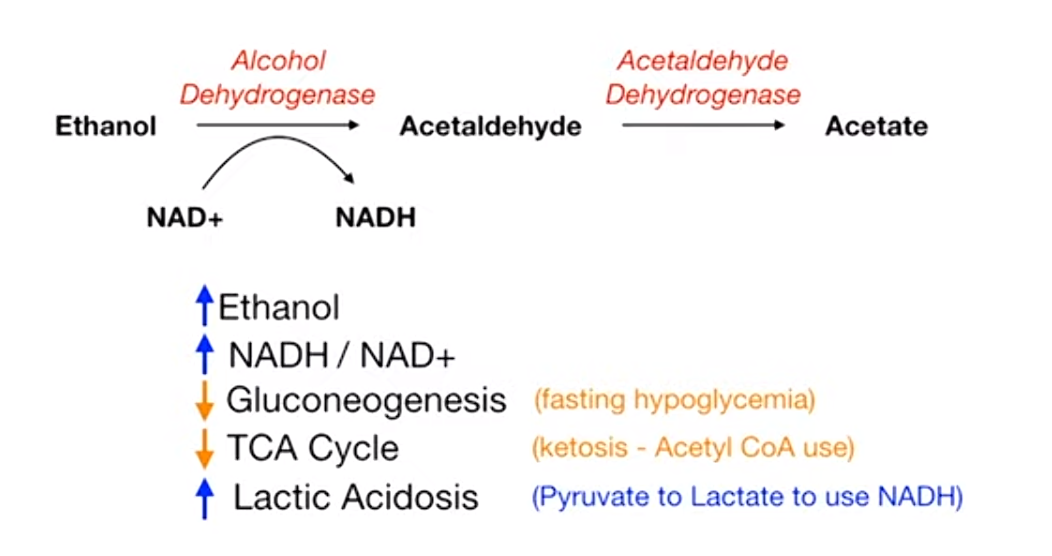
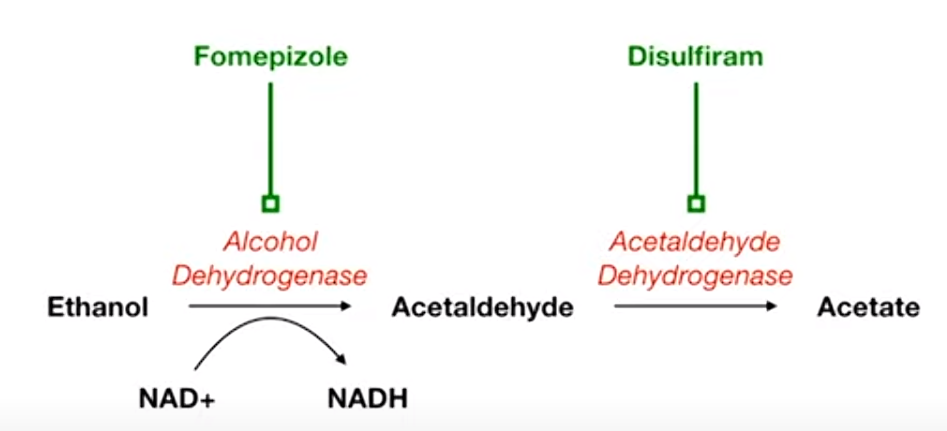
Mnemonic
- Fomepizole: think it as Foam-epizole, which can turn the beer to a lot of foam and less liquid (dehydro).
- Disulfiram: diSUFFERam. It can increase acetaldehyde and make people sick and dizzy.
Alcohol intoxication
Pathophysiology
- Mechanism
- GABA-A receptor agonist → Chronic use causes downregulation of GABA-A receptors → decreased GABA-A activity when cessation
- NMDA glutamate antagonist → chronic use causes upregulation of NMDA receptors → increased glutamate NMDA activity when cessation
- Absorption: The majority of alcohol consumed is absorbed by the proximal small intestine; only a small amount of alcohol is absorbed by the oral, esophageal, and/or gastric mucosa.
Clinical features
Altered consciousness, cognition, perception, judgment, affect, and/or behavior.
Diagnostics
- Routine laboratory studies that support the diagnosis include:
- Elevated osmolar gap
- The difference between the measured serum osmolarity and the calculated serum osmolarity. Normally, the calculated serum osmolarity is primarily determined by circulating levels of sodium salts (chloride and bicarbonate), glucose, and urea. An increased serum osmolar gap occurs when other solutes (e.g., ethanol, methanol, propylene glycol) are present in high enough concentrations to increase the measured osmolarity by more than 10 mOsmol/L.
- Anion gap metabolic acidosis (e.g., ↓ pH, ↓ HCO3-)
- Elevated osmolar gap