- Definition: a rare, very aggressive vascular malignancy, arising from endothelial cells of blood or lymphatic vessels
- Epidemiology: peak incidence age > 70 years
- Etiology
- Radiation (e.g., radiation therapy)
- Chronic lymphedema: Classic association is Stewart-Treves syndrome (angiosarcoma arising in the context of chronic lymphedema, often in the ipsilateral arm of a pt post-mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection).
- Likely due to a combination of increased lymphatic proliferation, which increases the likelihood of malignant cells, and a decreased number of lymph nodes, which decreases the ability to remove the malignant cells.
- Chemicals: Vinyl chloride and arsenic are implicated in hepatic angiosarcoma.
- Clinical features
- Location
- More common in sun-exposed areas
- Usually occur on the head, neck, and breast
- May involve the internal organs (e.g., hepatic angiosarcoma)
- Lesion
- Blue/purple-colored with a bruise-like appearance
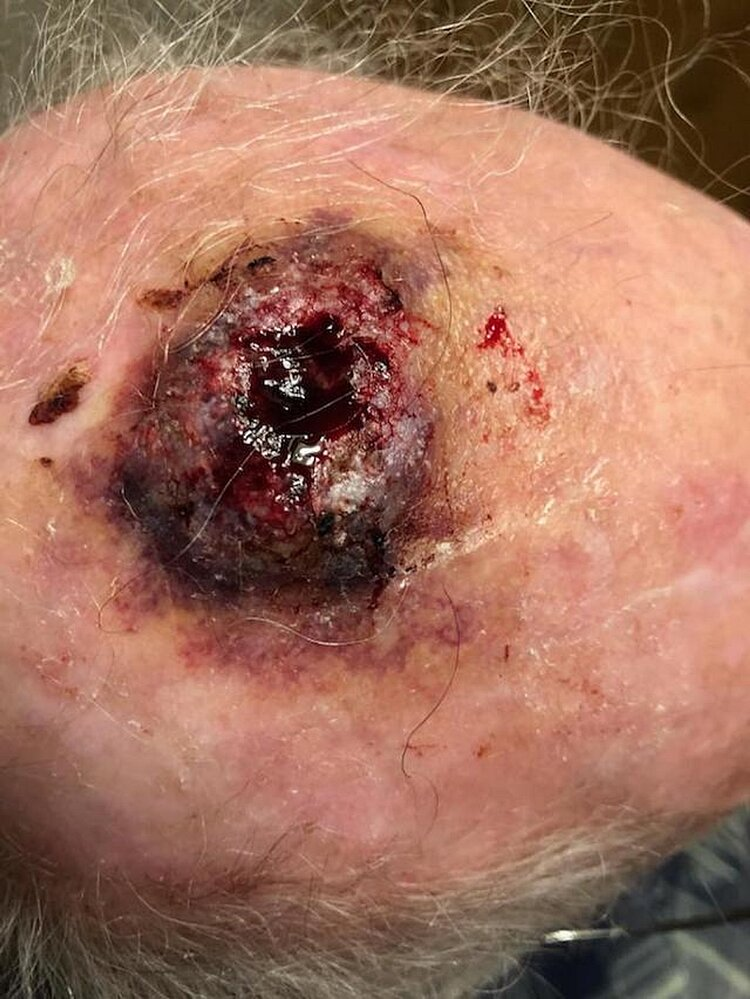
- Later stage: hemorrhage or ulceration
- High variability in appearance
- Prognosis & Treatment
- Very poor prognosis due to aggressive nature, high rate of local recurrence, and early hematogenous metastasis (often to the lungs).
- Tx: Wide surgical excision is the mainstay. Radiation and chemotherapy have limited efficacy but may be used in an adjuvant setting.
