Definition
- Thyrotoxicosis: a hypermetabolic condition caused by an inappropriately high level of circulating thyroid hormones irrespective of the source.
- Hyperthyroidism: a condition characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland; can cause thyrotoxicosis
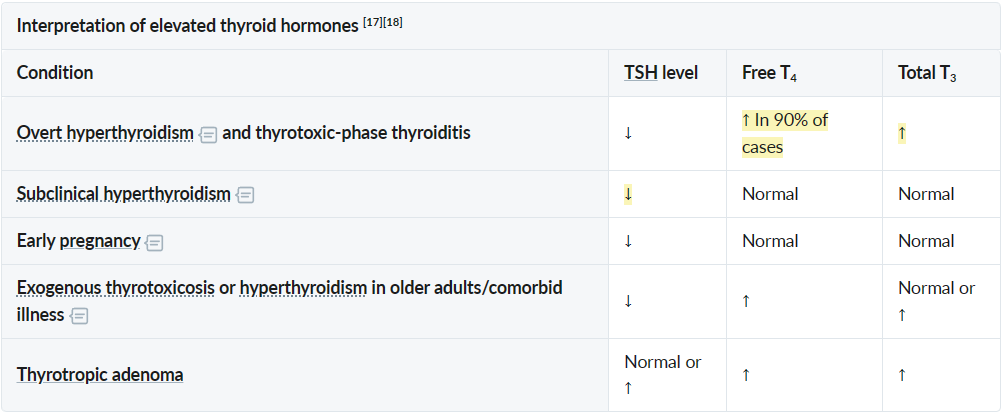
- Overt hyperthyroidism
- ↓ Serum TSH levels with ↑ serum free T4 and/or T3 levels
- Patients typically experience symptoms of thyrotoxicosis.
- E.g., Graves disease, toxic MNG, and toxic adenoma
- Subclinical hyperthyroidism
- ↓ Serum TSH levels with normal serum free T4 and T3 levels
- Patients are normally asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.
- May progress to overt hyperthyroidism
- If the negative feedback regulation mechanism is intact, increased T3 and T4 lead to TSH suppression, which in turn leads to reduced stimulation of thyroid follicular cells. Thyroid hormone levels may then be normal.
- Overt hyperthyroidism
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Secondary Causes (Rare)
- TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma: High TSH, High T3/T4 (TSH usually suppressed in primary causes).
- hCG-mediated: High hCG concentrations (e.g., Choriocarcinoma, Hydatidiform mole, Multiple gestation) cross-react with TSH receptors due to structural homology (alpha-subunit).
Pathophysiology
Thyroid hormone synthesis
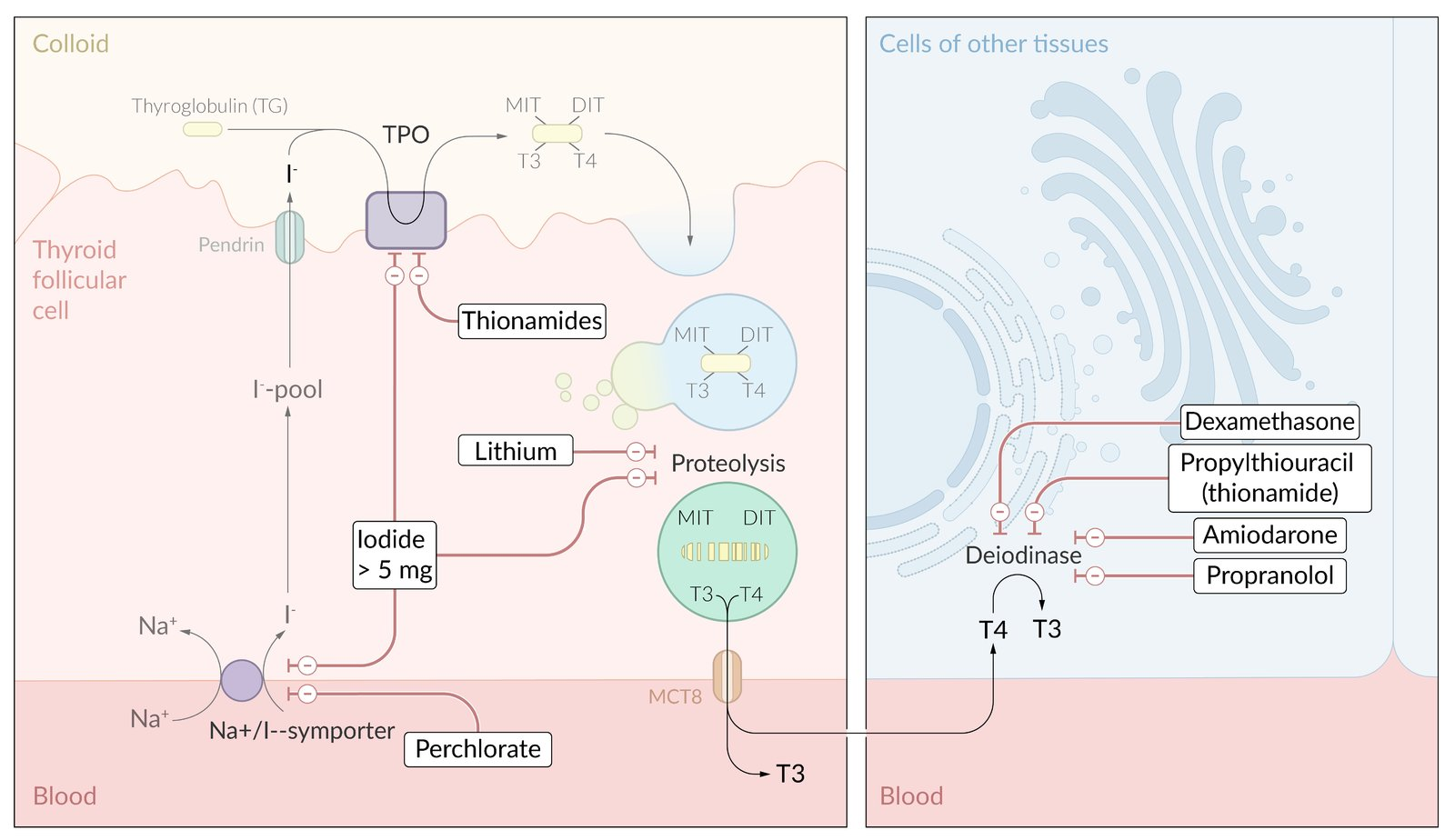
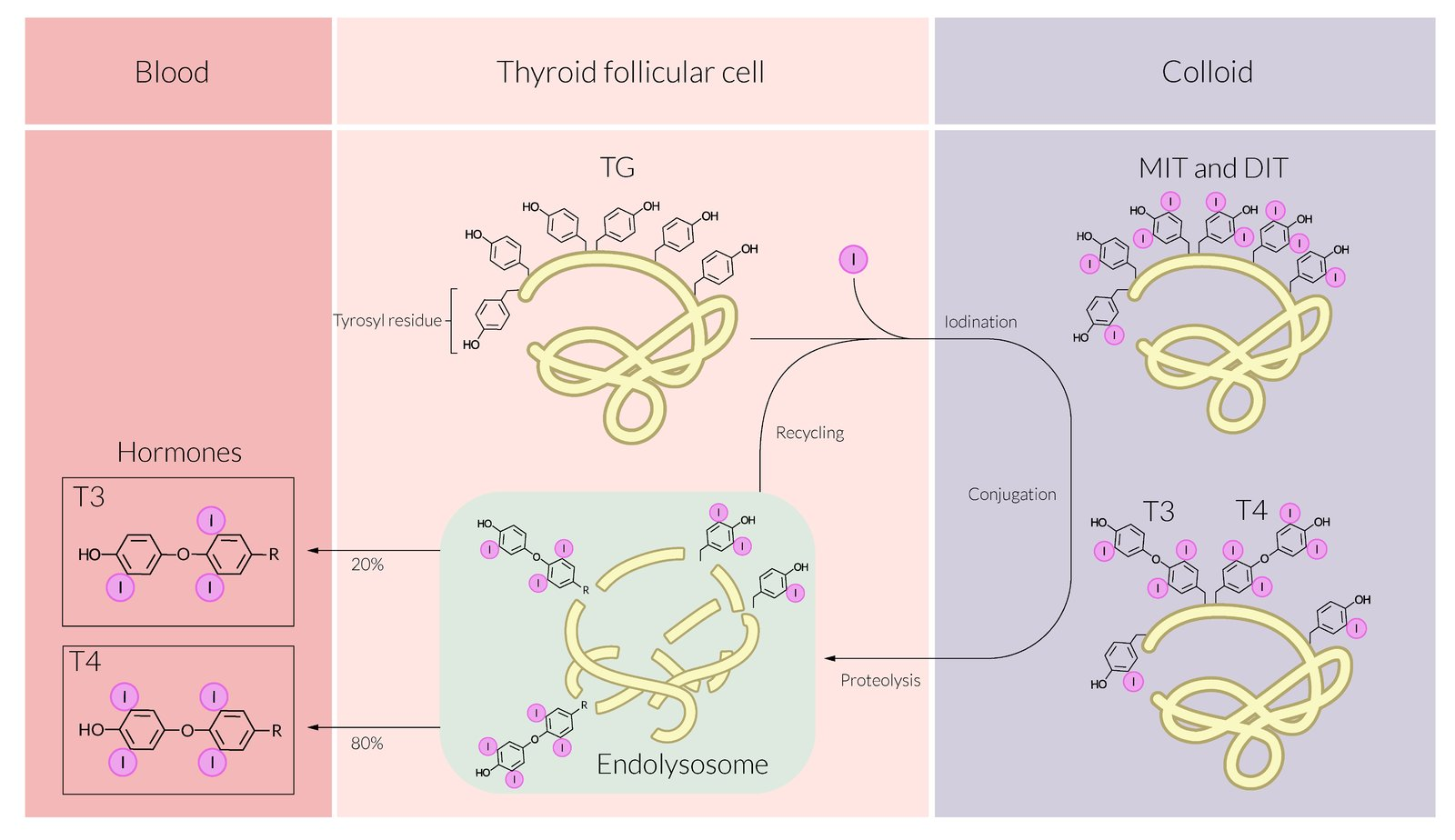
- Synthesis of thyroglobulin (TG)
- Uptake of iodide
- Iodination of thyroglobulin
- Thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
- Oxidation of iodide (I- → I2)
- Organification of the generated I2 by covalently linking it with the tyrosine residues present in TG.
- Generates single (TG + H2O2 + I2 = monoiodotyrosine, MIT) or double-iodinated species of tyrosine (TG-MIT + H2O2 + I2 = diiodotyrosine, DIT)
- Coupling reaction: conjugation of iodinated tyrosine residues
- Two DIT molecules form tetraiodothyronine: DIT + DIT = T4
- One MIT and one DIT form triiodothyronine: MIT + DIT = T3
- Thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
- Storage
- Release
- Transport
- Bound vs. Free: >99% of circulating thyroid hormone is bound to proteins (mainly TBG); <1% is free and physiologically active.
- Total T4 = Bound T4 + Free T4.
- Free T4 = Biologically active fraction; feedback inhibits TSH.
- Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG): Main carrier (binds ~70% of T4).
- TBG (Estrogen/Pregnancy/OCP) Total T4, Normal Free T4.
- TBG (Liver failure, nephrotic syndrome) Total T4, Normal Free T4.
- Transthyretin (Prealbumin): Binds T4 and Retinol.
- USMLE Buzzword: Amyloidosis.
- Senile Cardiac Amyloidosis: Deposition of wild-type transthyretin in heart (elderly).
- Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy: Deposition of mutated transthyretin.
- Albumin: High capacity, low affinity carrier.
- Bound vs. Free: >99% of circulating thyroid hormone is bound to proteins (mainly TBG); <1% is free and physiologically active.
Tip
- Changes in TBG alter Total T4/T3 but Free T4/T3 usually remains normal (euthyroid state) due to feedback regulation. t
- Patients remain clinically euthyroid.
Clinical features
- Musculoskeletal
- Fine tremor of the outstretched fingers
- Hyperthyroid myopathy: a condition of muscle weakness, pain, and atrophy associated with hyperthyroidism (e.g., from Graves disease, thyroiditis)
- Predominantly affects individuals > 40 years of age
- Can develop acutely or several weeks to months after the onset of hyperthyroidism.
- Typically affects proximal muscles (e.g., hip flexors, quadriceps) more than distal muscles
- Serum creatine kinase levels are most often normal
- Osteopathy: osteoporosis due to the direct effect of T3 on osteoclastic bone resorption, fractures (in the elderly)
- In long-standing hyperthyroidism
- Endocrinological
- Female: oligo/amenorrhoea, anovulatory infertility, dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Serum sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels are high in hyperthyroidism → low serum free (unbound) estradiol concentrations
- Male: gynecomastia, decreased libido, infertility, erectile dysfunction
- Female: oligo/amenorrhoea, anovulatory infertility, dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Diagnostics
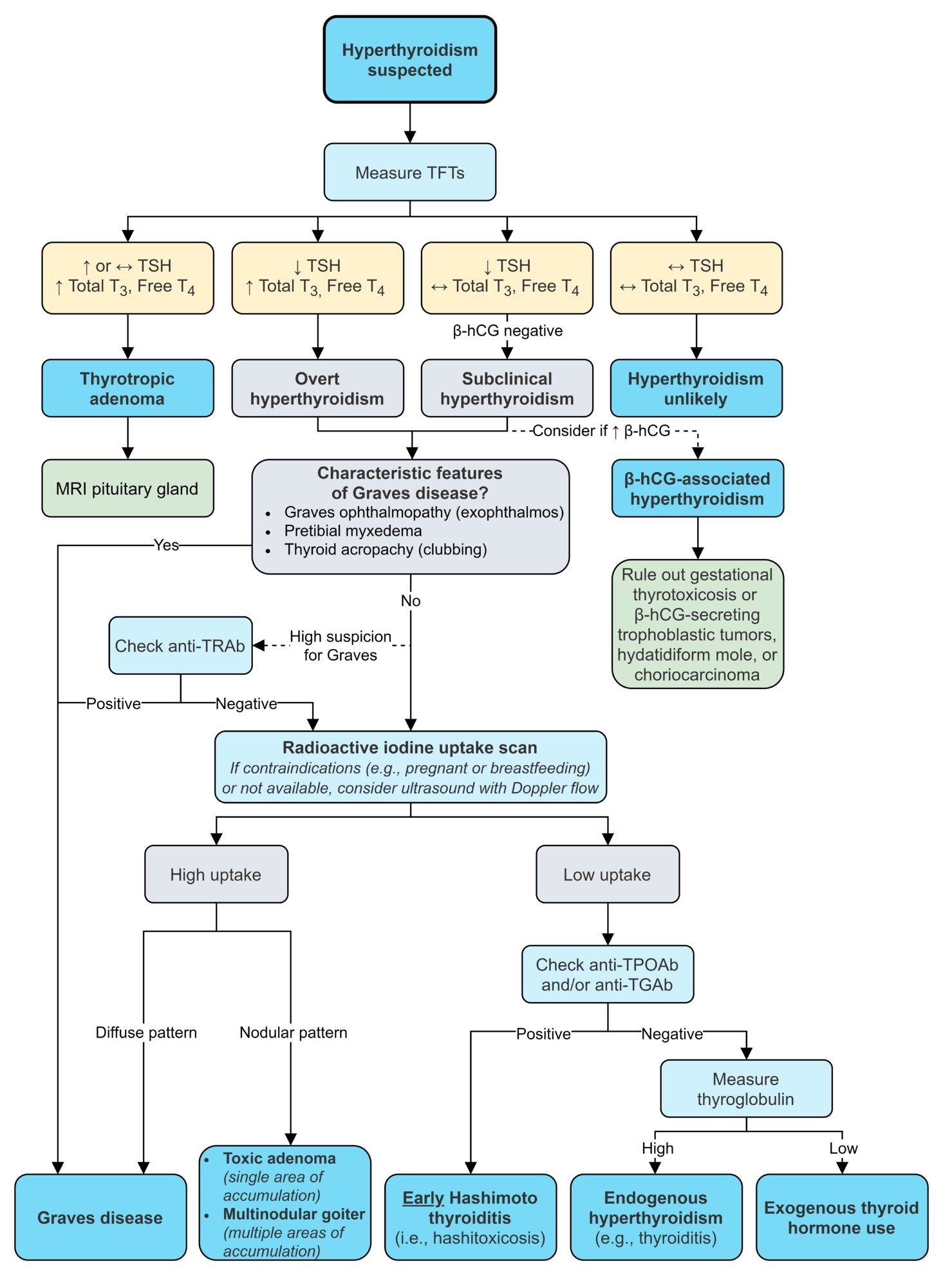
Nuclear medicine thyroid scan and radioactive iodine uptake measurement
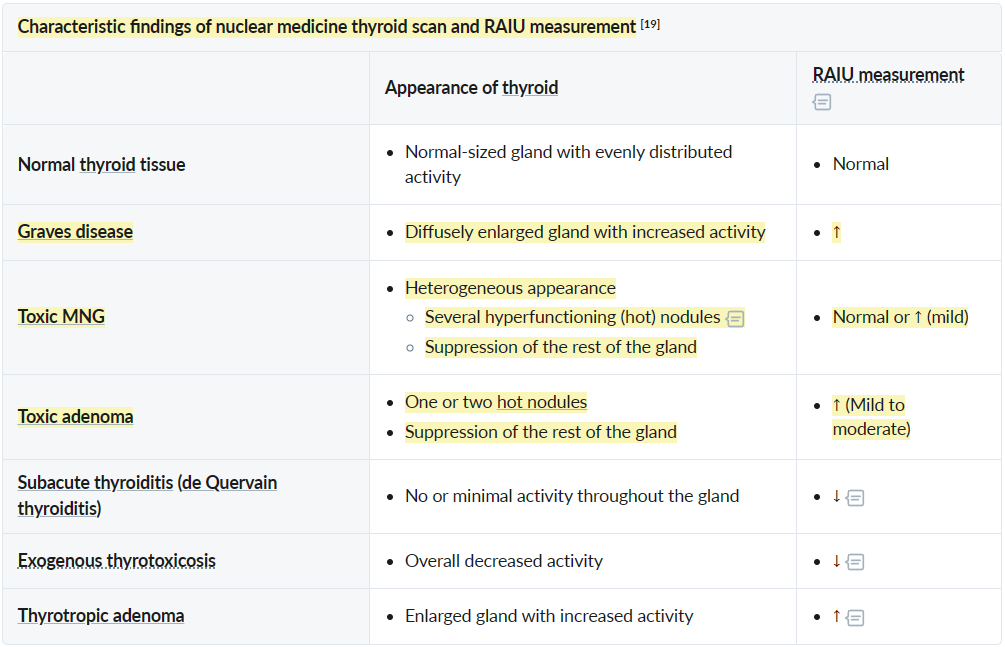
- Subacute thyroiditis: The inflammatory disruption of the follicle membranes inhibits the transport of iodine across the thyroid cells.
Treatment

Initial Symptomatic Control
- Beta-Blockers: Used for rapid relief of adrenergic symptoms (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety).
- Propranolol is frequently used as it is non-selective and also decreases peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. t
- Initiated as soon as hyperthyroidism is suspected and continued until definitive therapy takes effect.
Definitive Treatment Modalities
-
Thionamides (Antithyroid Drugs - ATDs)
- Drugs: Methimazole (MMI) and Propylthiouracil (PTU).
- MoA: Both inhibit thyroid peroxidase (TPO), blocking the organification and coupling steps of thyroid hormone synthesis. PTU additionally inhibits peripheral 5’-deiodinase, which decreases the conversion of T4 to the more active T3. t
- Indications: First-line therapy for Graves’ disease, especially in younger patients. Can also be used as a bridge to surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
- Key Side Effects:
- Common: Maculopapular rash.
- Severe (Rare): Agranulocytosis t (presents with fever, sore throat; requires immediate cessation of drug and CBC check), hepatotoxicity (higher risk with PTU), ANCA-associated vasculitis.
- MMI and PTU are both thionamide drugs. They carry a risk of cross-reactivity that can lead to agranulocytosis, so should this severe adverse reaction occur, both medications should be contraindicated.
- Hepatotoxicity (seen with propylthiouracil use)
- Teratogenicity: increased risk of congenital malformations with carbimazole and methimazole (e.g., aplasia cutis)
-
Radioactive Iodine (RAI / I-131) Ablation
- MoA: Oral I-131 is taken up by thyroid follicular cells, and the emitted beta particles induce fibrosis and destruction of the gland over weeks to months.
- Indications: Preferred treatment for Graves’ in many adults, toxic multinodular goiter, and toxic adenomas.
- Outcome: Leads to permanent hypothyroidism in most patients, requiring lifelong levothyroxine replacement.
- Contraindications: Absolute contraindications include pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is relatively contraindicated or used with caution in patients with moderate-to-severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy as it can worsen the condition.
-
Thyroidectomy (Surgical Removal)
- Indications: Patients with a very large goiter causing compressive symptoms, suspected or confirmed malignancy, severe ophthalmopathy, or when ATDs/RAI are contraindicated or refused.
- Pre-operative Preparation: Patients must be rendered euthyroid with ATDs. Potassium iodide solution (e.g., Lugol’s) may be given for 7-10 days pre-op to decrease the gland’s vascularity.
- Complications: Hypoparathyroidism (due to iatrogenic removal of parathyroid glands → hypocalcemia), recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (→ hoarseness), and superior laryngeal nerve injury.
Management in Special Situations
-
Thyroid Storm
- A life-threatening medical emergency requiring ICU admission.
- Treatment (The “4 P’s”):
- Propranolol (or other beta-blockers) to control adrenergic symptoms.
- Propylthiouracil (PTU) is often preferred as it blocks both hormone synthesis and peripheral T4-T3 conversion.
- Potassium Iodide (SSKI or Lugol’s solution) given at least 1 hour after ATD administration to block the release of pre-formed hormone.
- Prednisone (or other corticosteroids like hydrocortisone) to decrease peripheral T4-T3 conversion and treat potential relative adrenal insufficiency.
-
Pregnancy
- RAI is absolutely contraindicated.
- 1st Trimester: Propylthiouracil (PTU) is the preferred drug. Methimazole is associated with teratogenicity, including aplasia cutis and choanal atresia. t
- 2nd & 3rd Trimesters: Often switched to Methimazole (MMI) due to PTU’s higher risk of causing maternal hepatotoxicity.
- The goal is to maintain the mother’s free T4 at the high-normal range using the lowest possible dose of ATD.