Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- Binding of PR3-ANCA to PR3 activates neutrophils → release of neutrophilic inflammatory mediators, formation of neutrophil extracellular traps, complement activation → damage to endothelial cells of small blood vessels
Clinical features
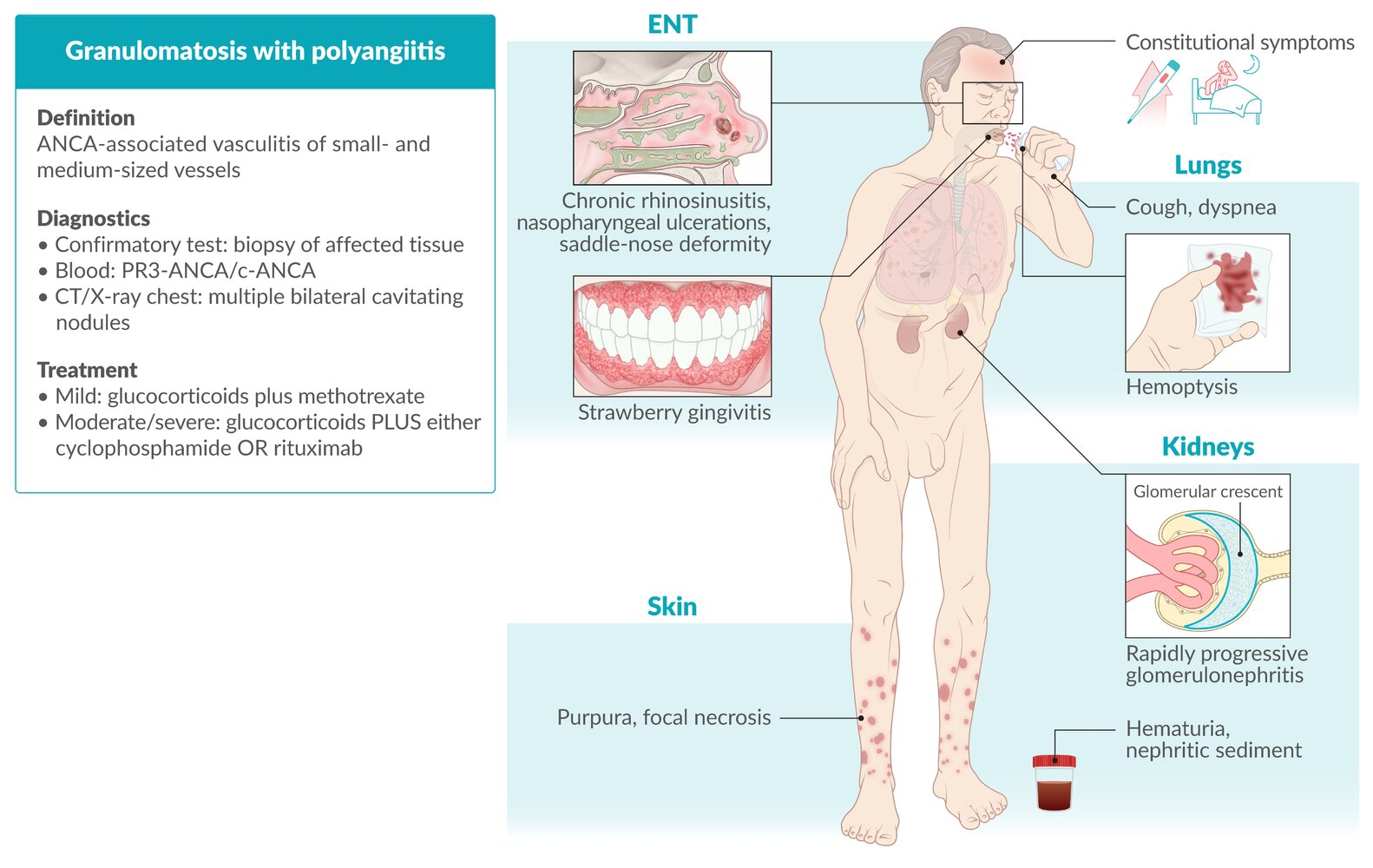
- ENT involvement: often the first clinical manifestation
- Chronic rhinitis/sinusitis: nasopharyngeal ulcerations → nasal septum perforation → saddle nose deformity
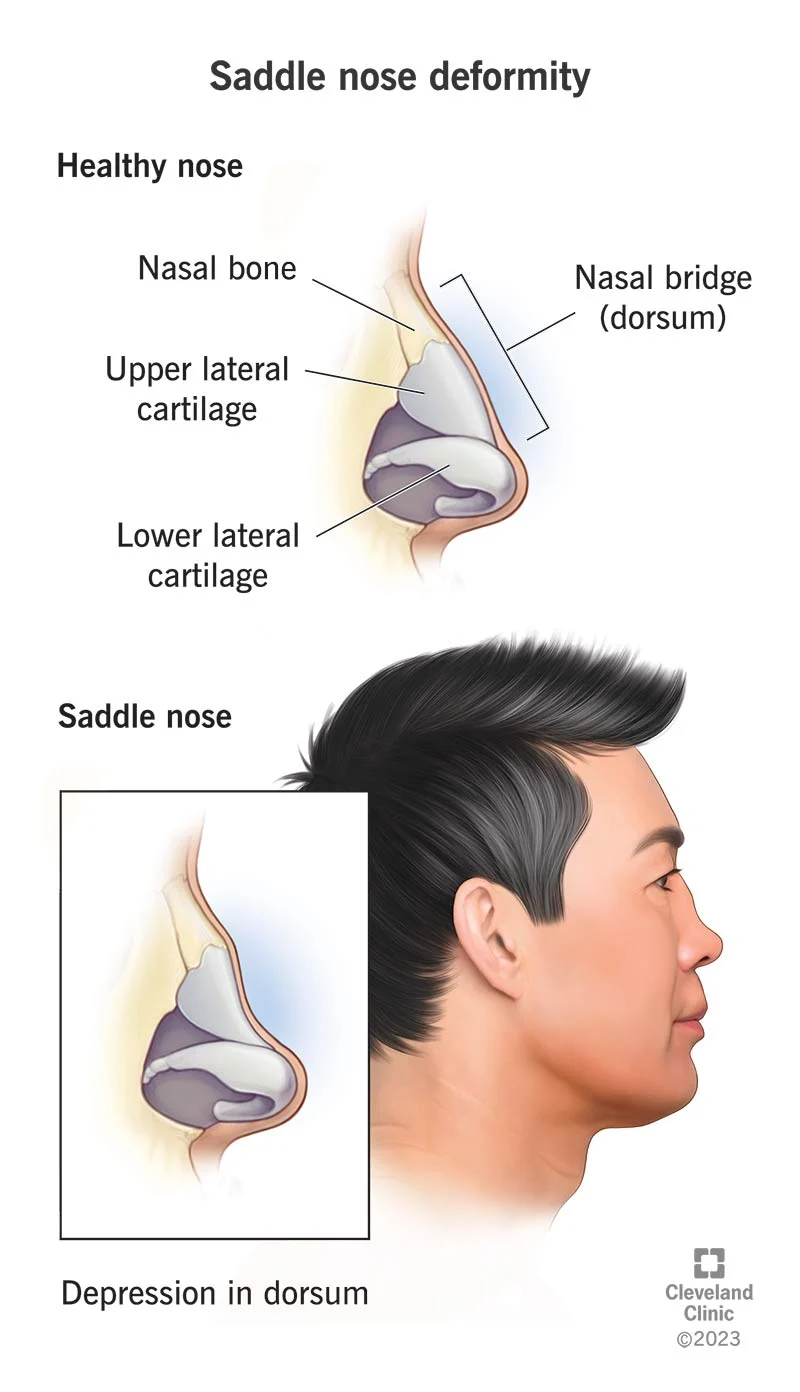
- Chronic rhinitis/sinusitis: nasopharyngeal ulcerations → nasal septum perforation → saddle nose deformity
- Lower respiratory tract: potentially life-threatening
- Renal involvement: potentially life-threatening
- Pauci-immune glomerulonephritis (Pauci‑immune indicates that there is little evidence of immune complex/antibody deposits.) → rapidly progressive (crescentic) glomerulonephritis (RPGN) with possible pulmonary-renal syndrome
- Usually spares GI
- Unlike PAN
Tip
Classic GPA triad: necrotizing vasculitis of small arteries, upper/lower respiratory tract manifestations, and glomerulonephritis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis)
Diagnostics
- Routine studies
- Urinalysis: microscopic hematuria, proteinuria
- Urine sediment: nephritic sediment (dysmorphic RBC and RBC casts)
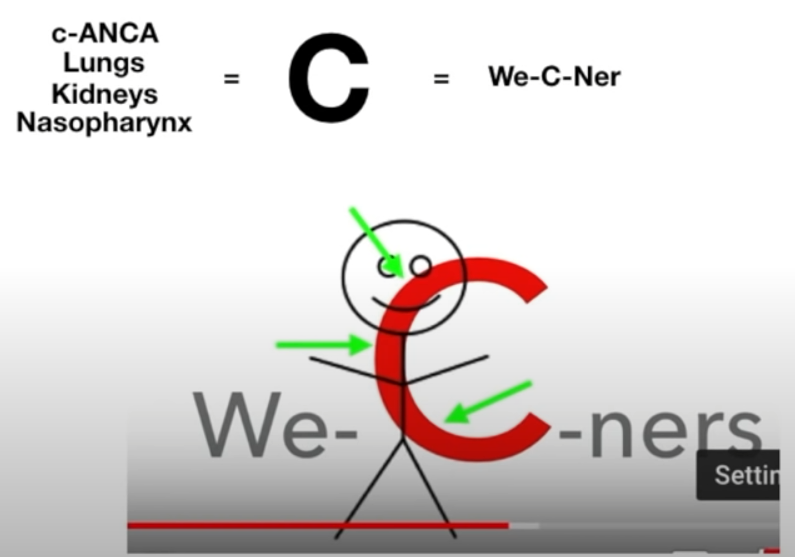
- Serology: ANCA (positive in ∼ 90% of patients)
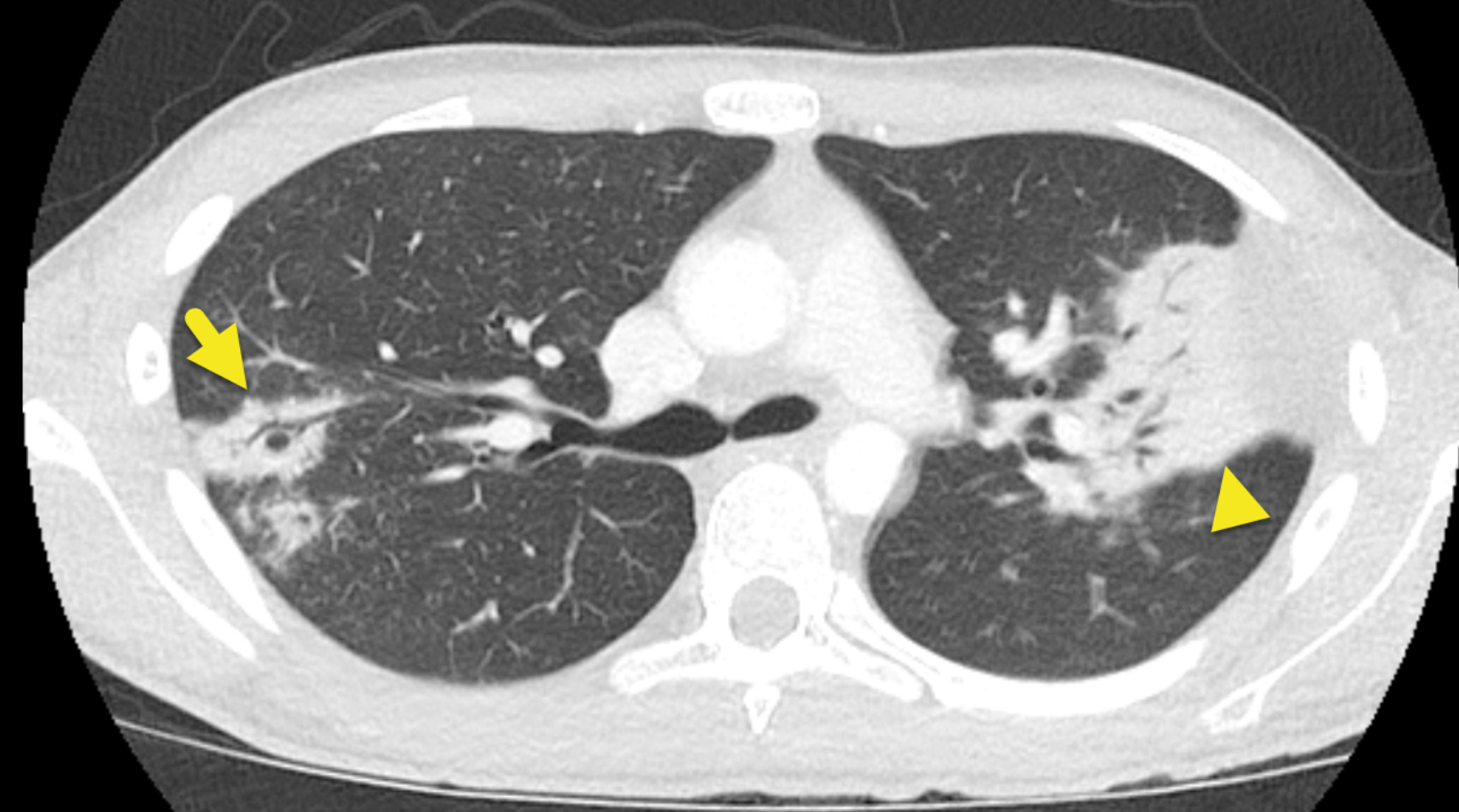
- Obtain a chest X-ray or CT chest
- Supportive findings
- Multiple bilateral cavitating nodular lesions
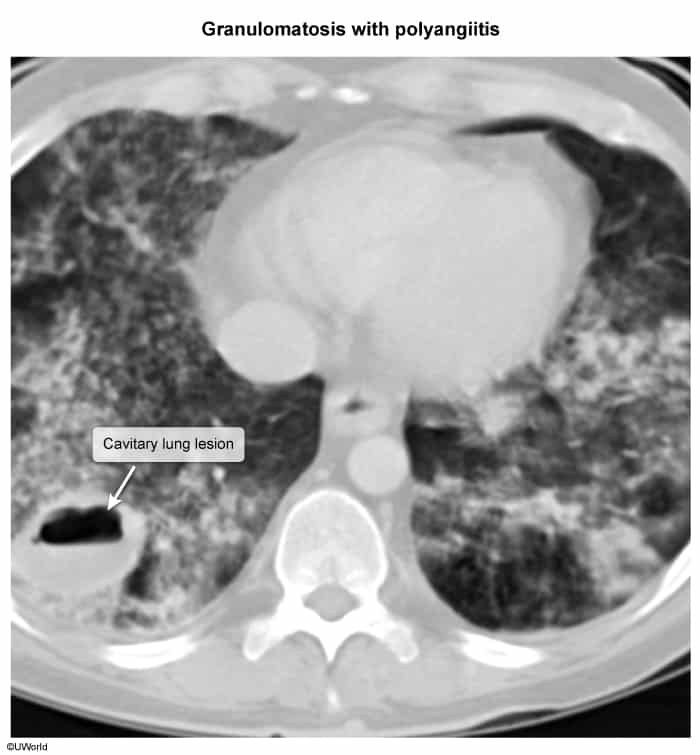
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
- Multiple bilateral cavitating nodular lesions
- Supportive findings
- Biopsy
- Necrosis
- Vasculitis of small and medium-sized vessels
- granulomas (mainly in the lungs and upper airways)
- necrotizing glomerulonephritis