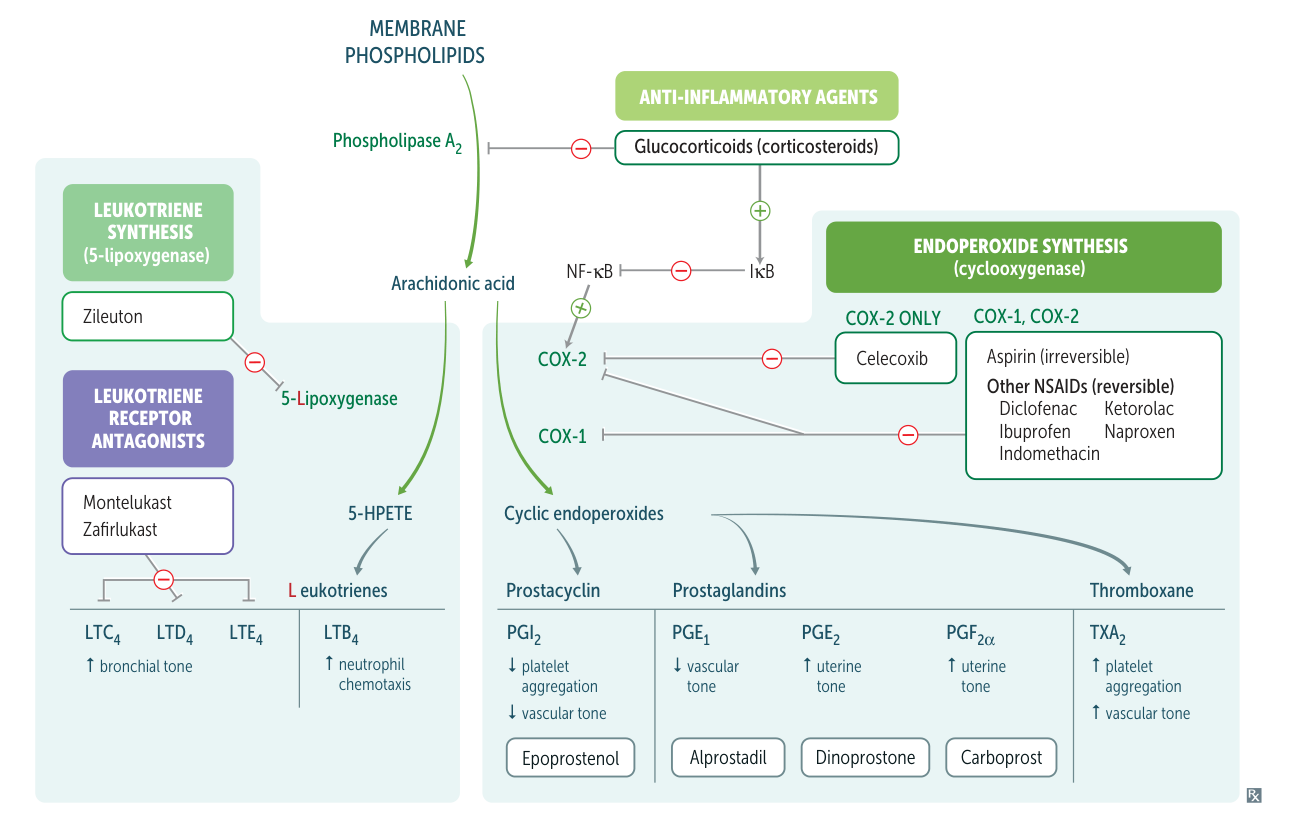
| Feature | Prostaglandins | Prostacyclin (PGI2) |
|---|
| Source | Derived from arachidonic acid | Derived from arachidonic acid |
| Function | Involved in various physiological processes, including inflammation, pain, and regulation of blood flow | Primarily functions as a vasodilator and inhibits platelet aggregation |
| Types | Several types (e.g., PGE2, PGF2α) | One main type: PGI2 |
| Receptors | Multiple receptors (e.g., EP, FP, DP) | Specific receptors (IP receptors) |
| Effects on Blood Vessels | Can cause vasodilation or vasoconstriction depending on the type | Causes vasodilation |
| Effects on Platelets | Can stimulate platelet aggregation (e.g., thromboxane A2) | Inhibits platelet aggregation |
| Role in Inflammation | Key mediators in the inflammatory response | Less direct role in inflammation |
| Half-life | Short half-life (minutes) | Short half-life (minutes) |
| Clinical Relevance | Used in various treatments (e.g., labor induction, gastric protection) | Used in treating pulmonary hypertension and cardiovascular diseases |
