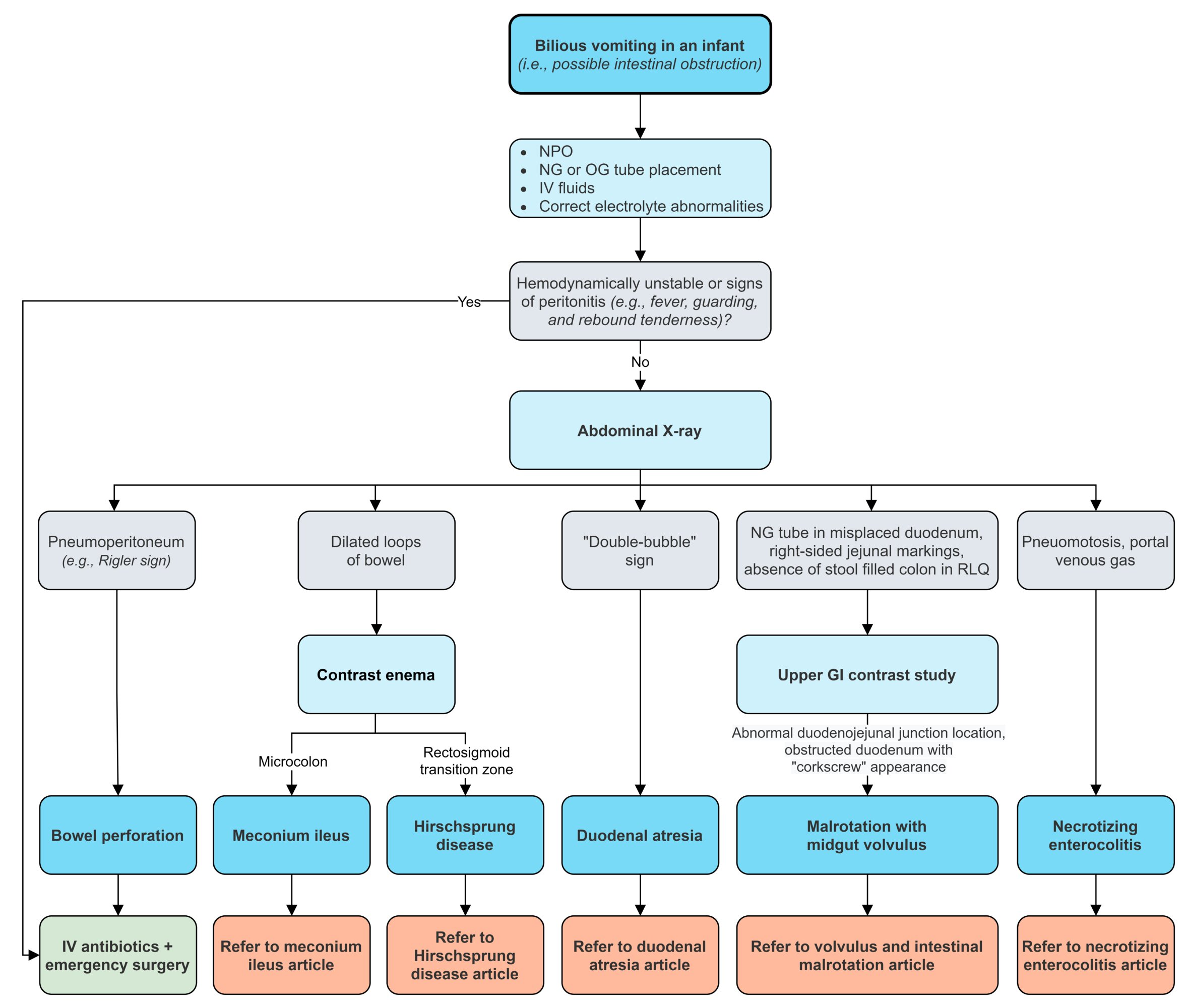
Tip
The pathophysiology of intestinal atresia varies based on the segment of bowel involved. In duodenal atresia, the mechanism involves failure of the lumen to recanalize after epithelial proliferation in the first trimeste. In contrast, intestinal atresia of the midgut (eg, jejunum, ileum, proximal colon) is the result of vascular occlusion in utero.
- Etiology/Pathophysiology
- Duodenal Atresia: Caused by a failure of recanalization of the duodenal lumen during the 8th-10th week of gestation.
- Jejunoileal/Colonic Atresia: Results from a vascular accident in utero (e.g., ischemia, volvulus, intussusception). This leads to necrosis and resorption of the affected bowel segment. t
- Associations
- Duodenal Atresia: Strong association with Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) (approx. 30-40%). Also associated with cardiac defects and annular pancreas.
- Jejunoileal Atresia: Associated with cystic fibrosis (especially meconium ileus), gastroschisis, and malrotation.
- Clinical Features
- Presents within the first 1-2 days of life.
- Bilious vomiting is a cardinal sign, especially with obstructions distal to the ampulla of Vater.
- Abdominal distension: More pronounced with more distal obstructions (e.g., ileal atresia).
- Failure to pass meconium within the first 24 hours.
- Prenatal finding: Polyhydramnios (excess amniotic fluid) is common because the fetus cannot swallow and absorb the fluid. This is more frequent in duodenal atresia.
- Diagnostics
- Prenatal Ultrasound: May show polyhydramnios and a dilated bowel. Can sometimes identify the “double bubble” sign in utero.
- Postnatal Abdominal X-ray:
- Duodenal Atresia: Classic “double bubble” sign, representing air trapped in the stomach and the proximal duodenum, with no distal gas.
- Air and fluid build up proximal to the obstruction and are separated by the pyloric sphincter, which resembles two bubbles on imaging, one in the stomach and one in the duodenum.
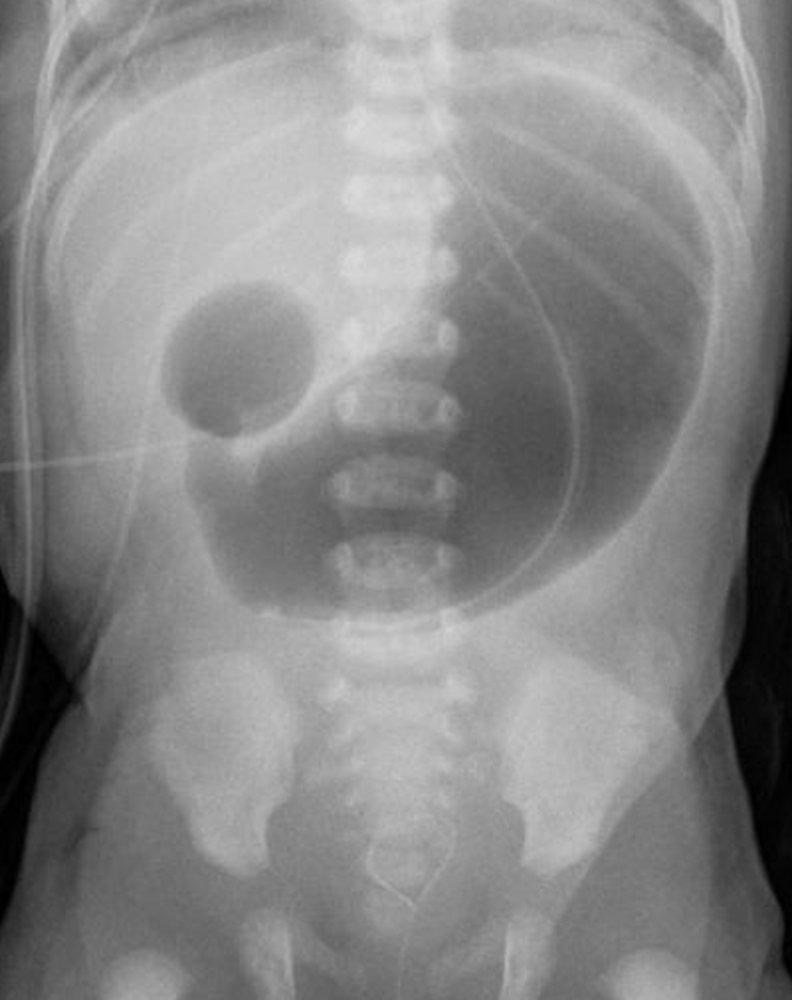
- Air and fluid build up proximal to the obstruction and are separated by the pyloric sphincter, which resembles two bubbles on imaging, one in the stomach and one in the duodenum.
- Jejunoileal Atresia: Dilated loops of small bowel with air-fluid levels and an absence of gas in the colon.
- Duodenal Atresia: Classic “double bubble” sign, representing air trapped in the stomach and the proximal duodenum, with no distal gas.
- Contrast Studies: An upper GI series or a contrast enema can help confirm the level of obstruction.
- Types & Specifics
- Duodenal Atresia: Most common type of intestinal atresia. Obstruction is located in the first part of the small intestine.
- Jejunoileal Atresia: Second most common type. Can present with multiple atretic segments (“string of sausages” or Type IV) or a spiral configuration around a single vessel (“apple-peel” or Type IIIb). The apple-peel deformity occurs with occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery.
- Colonic Atresia: The rarest form, accounting for less than 15% of cases.
- Treatment
- Initial Stabilization:
- Placement of a nasogastric (NG) or orogastric (OG) tube for decompression of the stomach and to prevent aspiration.
- IV fluids and parenteral nutrition are crucial due to inability to feed orally.
- Surgical Correction: Definitive treatment is surgery to resect the atretic segment and create an anastomosis (reconnection) of the bowel.
- For duodenal atresia, a duodenoduodenostomy is typically performed.
- Initial Stabilization:
- Complications
- Short bowel syndrome: If a significant length of intestine must be resected, leading to malabsorption.
- Postoperative complications can include anastomotic leak or stricture.
Differential diagnostics