| Feature | Aerobic Glycolysis | Anaerobic Glycolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Final Product | Pyruvate | Lactate |
| Net ATP | 2 ATP | 2 ATP |
| Net NADH | 2 NADH | 0 NADH |
| NAD+ Regeneration | ETC (requires O₂) | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| Total ATP/Glucose | ~32 ATP (including TCA/OxPhos) | 2 ATP |
| Location | Cytoplasm → Mitochondria | Cytoplasm only |
| Rate | Slower | Faster |
- Pathway Overview
- Function: Primary pathway for glucose metabolism to produce ATP and intermediates for other pathways.
- Location: Cytosol of all cells.
- Oxygen Requirement: Can function aerobically (pyruvate → acetyl-CoA → TCA cycle) or anaerobically (pyruvate → lactate).
- Phases:
- Investment Phase: Consumes 2 ATP.
- Payoff Phase: Generates 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
- Net Products (per 1 glucose molecule)
- 2 Pyruvate
- 2 ATP (net)
- 2 NADH
- Fate of Products:
- Aerobic Glycolysis
- Pyruvate: Transported into the mitochondria. Converted to Acetyl-CoA by the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) complex.
- NADH: “Shuttled” into the mitochondria (e.g., malate-aspartate, glycerol-3-phosphate shuttles) to donate electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC).
- Anaerobic Glycolysis
- Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) converts pyruvate to lactate, oxidizing NADH to NAD+.
- This regeneration of NAD+ is the critical step, as NAD+ is required for the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase step of glycolysis to continue.
- Aerobic Glycolysis
- Irreversible/Regulatory Enzymes (High-Yield)
- 1. Hexokinase / Glucokinase
- Reaction: Glucose → Glucose-6-Phosphate. Traps glucose inside the cell.
- Hexokinase: Found in most tissues. ↓ Km (high affinity), ↓ Vmax. Inhibited by its product, Glucose-6-P.
- Glucokinase: Found in liver & pancreatic β-cells. ↑ Km (low affinity), ↑ Vmax. Functions as a glucose sensor. Induced by insulin. Not inhibited by Glucose-6-P.
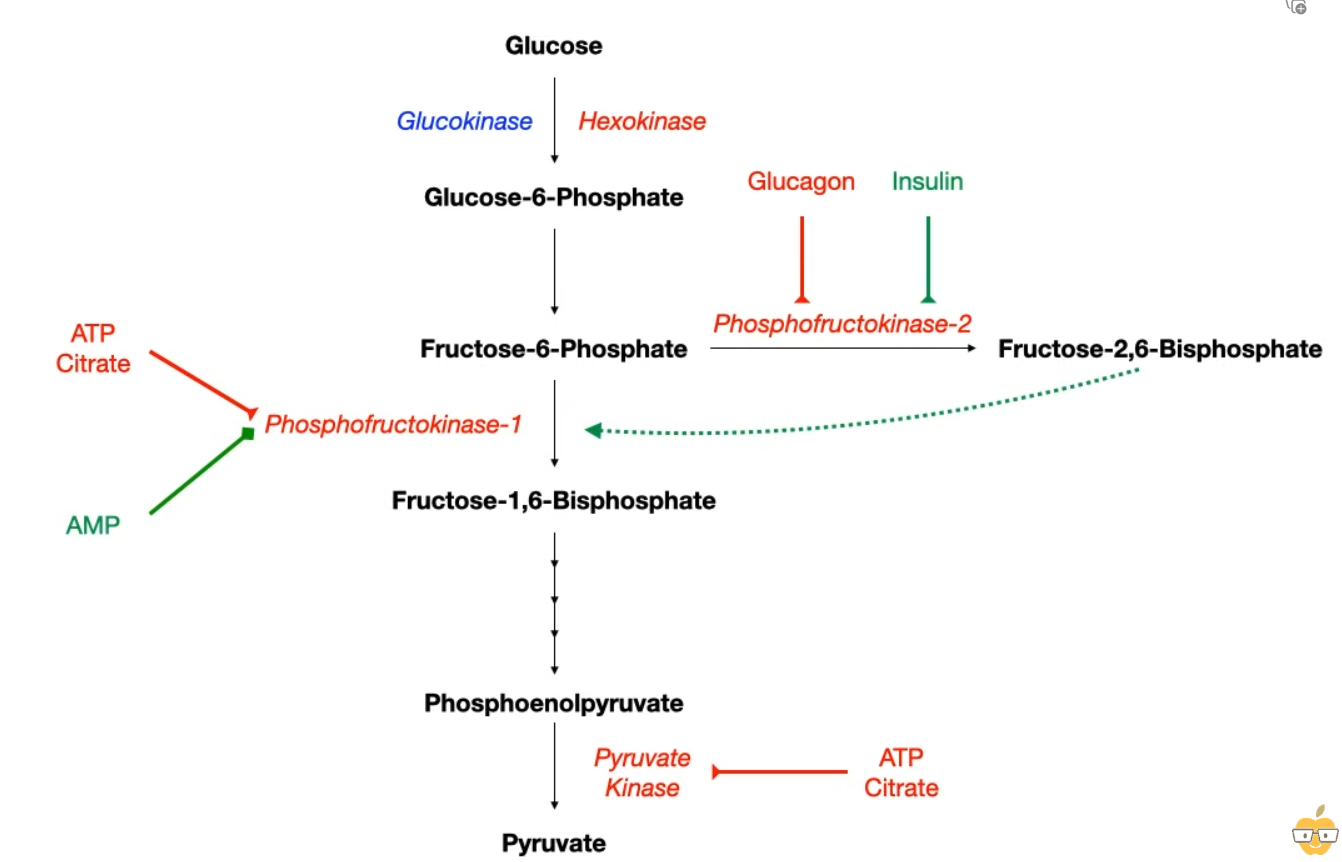
- 2. Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
- Reaction: Fructose-6-P → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- This is the main rate-limiting step of glycolysis.
- Activators:
- AMP (signals low energy state).
- Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (most potent activator).
- Inhibitors:
- ATP (signals high energy state).
- Citrate (signals sufficient TCA cycle intermediates).
- 3. Pyruvate Kinase
- Reaction: Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) → Pyruvate. Generates ATP via substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Activators:
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (feed-forward activation).
- Inhibitors:
- ATP
- Alanine
- 1. Hexokinase / Glucokinase
- Regulation of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP)
- Controls the switch between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
- Synthesized/degraded by a bifunctional enzyme (PFK-2/FBPase-2).
- Fed State (↑ Insulin): Dephosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2. PFK-2 domain is active → ↑ F-2,6-BP → ↑ PFK-1 activity → Glycolysis favored.
- Fasting State (↑ Glucagon): Phosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2 via PKA. FBPase-2 domain is active → ↓ F-2,6-BP → ↓ PFK-1 activity → Gluconeogenesis favored.
- Clinical Correlations
- Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
- Autosomal recessive disorder.
- Causes ↓ ATP production in RBCs → membrane failure → extravascular hemolytic anemia.
- RBCs swell and are cleared by the spleen (splenomegaly).
- Findings: Burr cells (echinocytes) on peripheral smear.
- Arsenic Poisoning
- Inhibits enzymes requiring lipoic acid, primarily the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH), blocking entry of pyruvate into the TCA cycle.
- Also inhibits glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, preventing ATP production in glycolysis without stopping the pathway (produces 0 net ATP).
- Lactic Acidosis
- Occurs in states of tissue hypoxia (e.g., ischemia, shock) where pyruvate is shunted to lactate via lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) to regenerate NAD+ for continued glycolysis.
- Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency