Etiology
- Most likely genetic predisposition to autoimmune reaction (associated with HLA-DR3 and HLA-DQ2)
- Associated with celiac disease and sensitivity to potassium iodide (e.g., contrast medium)
Clinical features
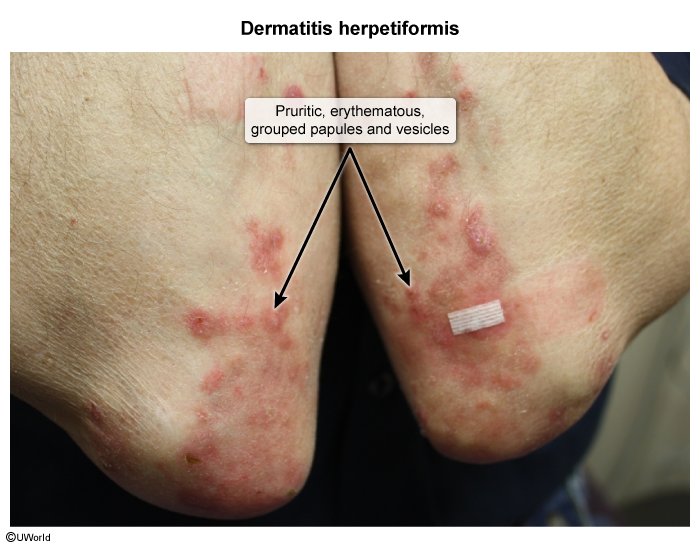
- Tense, grouped subepidermal vesicles, papules, and/or bullae (herpetiform appearance)
- Intense pruritus
- Bilateral, symmetrical distribution, commonly over elbows, knees, buttocks, shoulders, scalp
- No mucosal involvement
Diagnostics
- IgA autoantibodies against tissue transglutaminase
- Histology and immunohistochemistry
- Subepidermal vesicle formation
- Neutrophilic papillary microabscesses
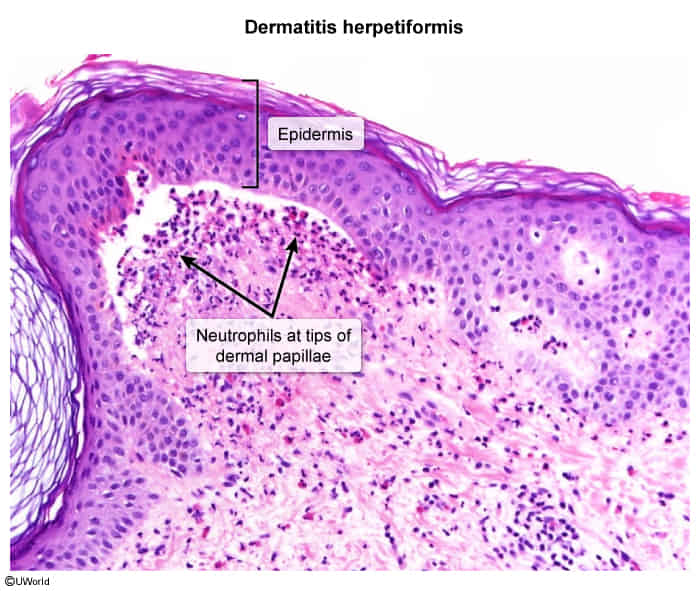
- Deposition of granular IgA in dermal papillae

