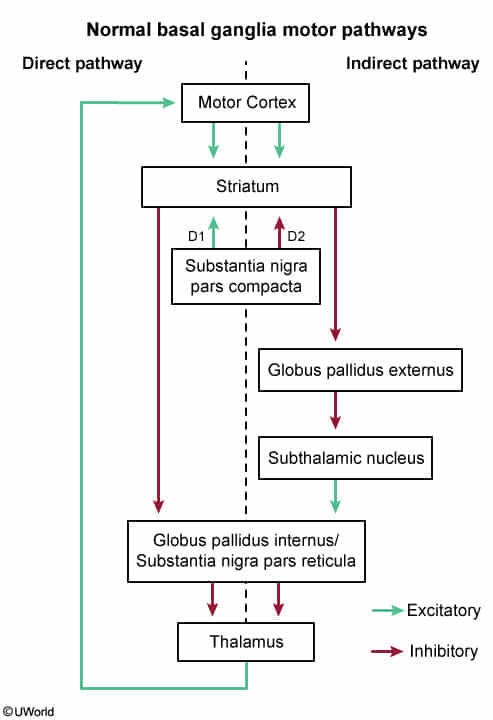
The purpose is to regulate the activity of motor cortex, using thalamus.
Transclude of Drawing-2025-03-24-09.33.38.excalidraw
- Direct pathway: Starts with cortical excitation of D1-receptor-expressing Medium Spiny Neurons (MSNs) in the Striatum.
- D1 Receptor: Dopamine binds to and activates the D1 receptor. The consequence of this activation is typically excitatory for the neuron (e.g., increased cAMP, making it more likely to fire).
- Like an air conditioner that cools the room (inhibits GPi). Dopamine makes the AC run stronger. Removing dopamine makes the AC weaker.
- Indirect pathway: Starts with cortical excitation of D2-receptor-expressing Medium Spiny Neurons (MSNs) in the Striatum.
- D2 Receptor: Dopamine binds to and activates the D2 receptor. The consequence of this activation is typically inhibitory for the neuron (e.g., decreased cAMP, making it less likely to fire).
- Like a heater that warms the room (excites GPi). Dopamine turns the heater down. Removing dopamine lets the heater run hotter.
Mnemonic
The direct pathway Comes Straight Into the Thalamus:
- Cortex → Striatum → Internal GP → Thalamus.
The indirect pathway Comes Straight, Exits, then Sidesteps Into the Thalamus:
- Cortex → Striatum → External GP → STN → Internal GP → Thalamus.