Strabismus caused by paresis (partial failure of action) or paralysis (total failure of action) of one or more extraocular muscles (ophthalmoplegia)
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Neuropathies: CN III, CN IV, CN VI palsies
- Demyelinating disease (e.g., multiple sclerosis)
- Myopathies (e.g., myasthenia gravis, ocular myopathies, restrictive thyroid myopathy)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
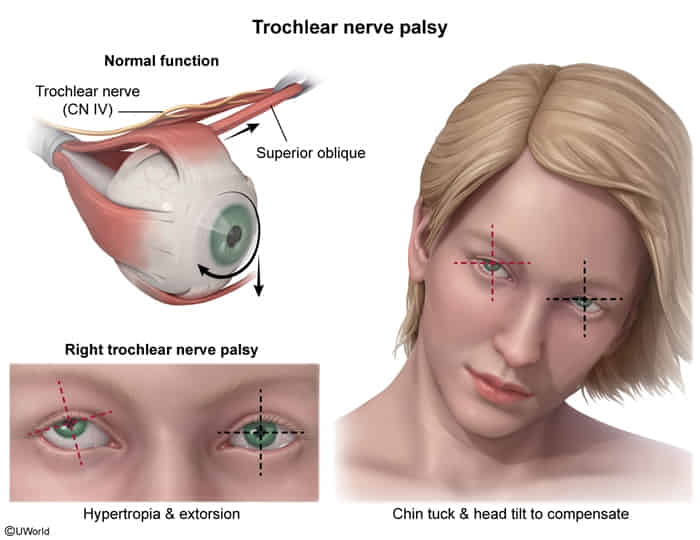
- Diplopia (double vision): most pronounced when looking in the direction usually enabled by the paralyzed muscle
- Often compensatory head posture
- Impaired extraocular muscle function